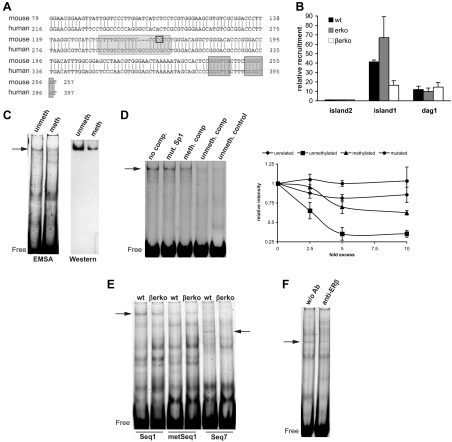
Fig. 5.
Sp1 binding to the Glut4 promoter. A, Alignment of human and mouse Glut4 promoter sequence using BLAST. CpG11 (marked by a black rectangle) lies in a conserved region in the Glut4 promoter and is part of an Sp1-binding site (light gray shading). Marked with dark gray shading is the LXR-binding site. B, ChIP assays for Sp1 in wt, erko, and βerko MEFs. ChIPs were analyzed by real-time PCR (right panel). Real-time PCR results were normalized to inputs and recruitment to CpG island 2. Real-time PCR data are represented as mean ± sd. C, Mobility shift assays (left panel) and Western blot of the gel shifts (right panel) using nuclear extracts of wt MEFs and labeled unmethylated or methylated Seq1 oligonucleotides. Unmeth, Unmethylated probe; meth, methylated probe. Shown are representative gels and blots of three independent assays. D, Competition assays on labeled unmethylated Seq1 with 5-fold excess of different unlabeled oligonucleotides. Left panel, shows representative gel. Lane 1, No competitor; lane 2, 5× Seq1 with mutated Sp1 site; lane 3, 5× methylated Seq1; lane 4, 5× unmethylated Seq1; lane 5, unmethylated Sp1 control. Right panel shows quantification of at least three independent competition assays with different concentrations of an unrelated oligonucleotide (rhombes), unmethylated Seq1 (squares), methylated Seq1 (triangles), and Seq1 with mutated Sp1 site (circles). Shown are means ± sd. E, Mobility shift assays using nuclear extracts of wt and βerko MEFs with Seq1 (lanes 1 + 2), methylated Seq1 (lanes 3 + 4), and Seq7 (lanes 5 + 6). F, Mobility shift assays using wt extracts and Seq7 in the absence (lane 1) and presence (lane 2) of 1 μg anti-ERβ antibody. Ab, Antibody.