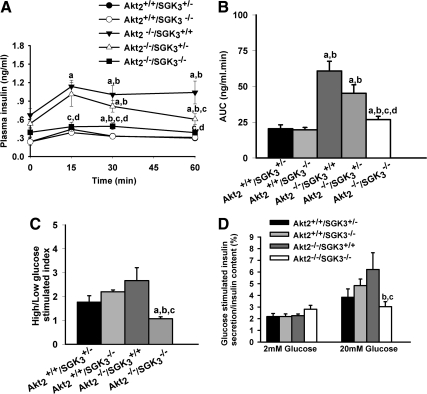
Fig. 7.
DKO mice have reduced in vivo and in vitro glucose-stimulated insulin secretory capacity. A and B, In vivo glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Glucose (1 g/kg) was administered ip to overnight fasted male mice. A, Plasma insulin levels were monitored at 0, 15, 30, and 60 min (n = 10 animals per group). B, Quantification of plasma insulin excursions as area under the curve (AUC). C and D, In vitro glucose-stimulated insulin secretory capacity: male mice (7–9 wk of age) were fasted overnight, and islets were isolated and incubated in 2 mm glucose for 10 min and then in 20 mm glucose for another 10 min. C, Insulin secretion index was calculated as ratio of normalized insulin secretion in high glucose to normalized insulin secretion in low glucose. D, Insulin levels under low- and high-glucose stimulation related to total cellular insulin content separately. Insulin secretion into medium and total cellular content were measured. Values shown are mean ± sem. a, P < 0.05 vs. Akt2+/+/SGK3+/−; b, P < 0.05 vs. Akt2+/+/SGK3−/−; c, P < 0.05 vs. Akt2−/−/SGK3+/+; d, P < 0.05 vs. Akt2−/−/SGK3+/−.