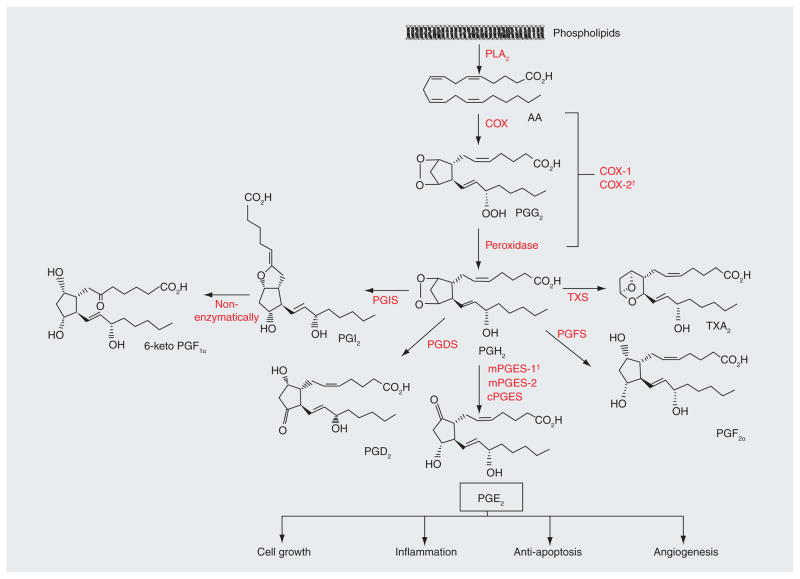
Figure 2. Prostaglandin E2 synthesis pathway.
The initial step of PGE2 synthesis is the stimulus-induced liberation of AA from the membrane phospholipids by PLA2 enzymes. AA is then sequentially metabolized into PGG2 and then to PGH2 by either COX-1 or COX-2. PGH2 is an unstable intermediate prostanoid, which is rapidly converted into various prostanoids by specific terminal prostaglandin synthases, of which prostaglandin E synthases (mPGES-1, mPGES-2 and cPGES) generate PGE2 from PGH2. The other synthases include PGIS that forms PGI2, PGDS for PGD2, PGFS for PGF2α and TXS for TXA2. PGI2 is non-enzymatically metabolized to the more stable 6-keto PGF1α. PGE2 mediates inflammation, stimulates cell growth and angiogenesis, and also inhibits apoptosis.
†Upregulated in cancers.
AA: Arachidonic acid; PGDS: Prostaglandin D synthase; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; PGFS: Prostaglandin F synthase; PGIS: Prostaglandin I synthase; PLA2: Phospholipase A2; TXA2: Thromboxane A2; TXS: Thromboxane synthase.