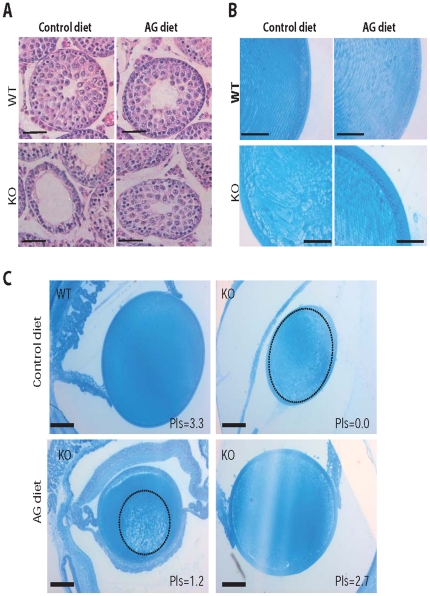
Figure 6. AG treatment in young mice prevents tissue pathology.
(A) Testis sections of P20 WT and Pex7 KO pups stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Whereas control-fed Pex7 KO pups already showed the degenerative changes in spermatocytes, AG-fed Pex7 KO pups where protected from degeneration and showed normal appearing seminiferous tubules and spermatocytes. Bars are 50 µm. (B) Eye sections of P20 WT and Pex7 KO pups stained with Richardson's stain. In contrast to the lens of WT pups showing organized and orientated fiber cells, the cataract in the lens of control-fed Pex7 KO pups shows abnormally sized and abnormally arranged fiber cells. The AG diet prevented the abnormal development of fiber cells in Pex7 KO pups thus preventing cataract formation. Bars are 50 µm. (C) Eye sections of mice showing the correlation between plasmalogen (Pls) levels and the development of cataracts in Pex7 KO pups (from each mouse one eye was used for histology and the other eye used for biochemical analyses). Whereas complete loss of plasmalogens (Pls = 0.0) leads to a massive cataract occupying the entire lens (the cataract area is circled with a dashed line), a plasmalogen level of 2.7% is able to prevent cataract formation in Pex7 KO pups. Partial restoration of plasmalogens (Pls = 1.2%) leads a small nuclear cataract (circled with a dashed line). Sections were stained as in (B) and bars are 100 µm. Numbers of mice analyzed: on control diet WT mice n = 4 and Pex7 KO mice n = 4, on AG diet WT mice n = 4 and Pex7 KO mice n = 6.