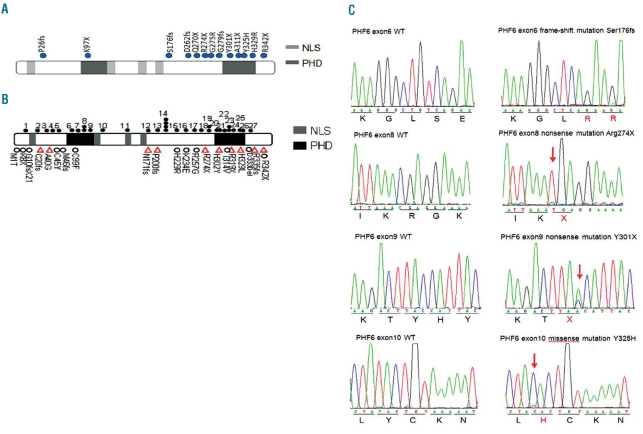
Figure 1.
PHF6 mutations in T-ALL. (A) Structure of the PHF6 protein, including four nuclear localization signals (NLS) and two imperfect PHD zinc-finger domains. Filled circles indicate PHF6 mutations. (B) PHF6 mutations previously reported in T-ALL, AML and BFLS. Filled circles represent mutations in T-ALL. Triangles represent mutations in AML. Open circles represent mutations in BFLS. 1, G10fs. 2, C28fs. 3, A41fs. 4, H43fs. 5, H44fs. 6, T98fs. 7, Y105fs. 8, R116X. 9, G122X. 10, H135fs. 11, S158fs. 12, F172fs. 13, S191fs. 14, C215F and C215Y. 15, R225X. 16, K235X. 17, R257X. 18, G263fs. 19, R274X. 20, C280Y. 21, C283R. 22, T300A. 23, Y303fs and Y303X. 24, A311P. 25, S320X. 26, H329R. 27, D333fs. (C) Representative DNA sequencing chromatograms of T-ALL genomic DNA samples showing mutations in exons 6, 8, 9 and 10 of PHF6.