Figure 1.
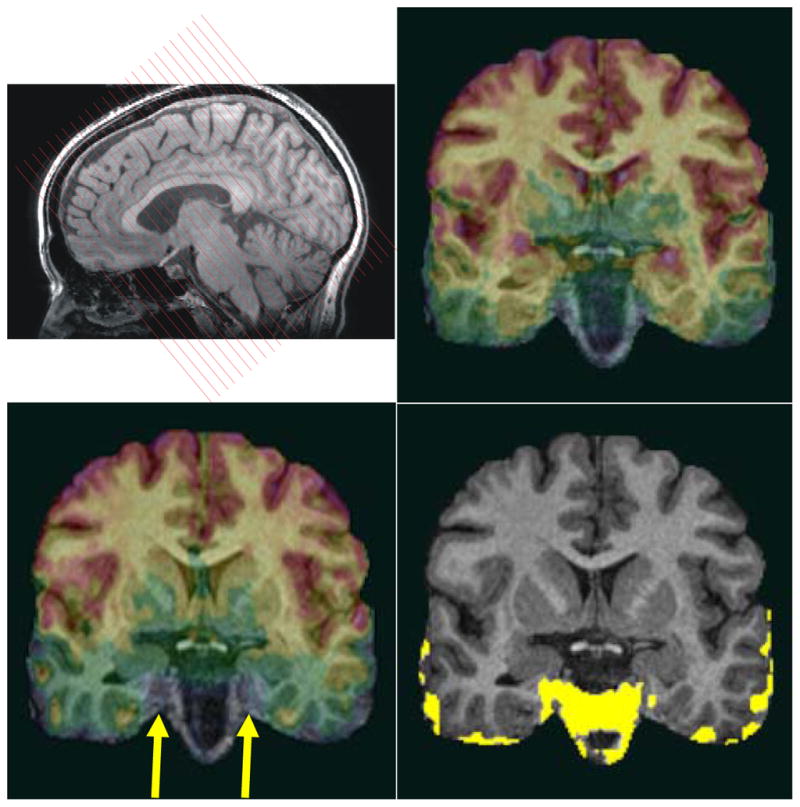
The functional EPIs were acquired perpendicular to the long axis of the hippocampus (top left). To show susceptibility drop-out artifacts of EPIs for different slice directions, we compare EPIs acquired in a coronal oblique orientation (top right) with EPIs acquired in a conventional axial orientation for a particular subject (lower left). All EPIs were co-registered to the same T1 3D-SPGR anatomical image (which serves here as an underlay). The yellow region (lower right) shows the difference of the EPI signal coverage of the coronal oblique and axial acquisition indicating major signal drop-off in anterior MTL regions (right CA1, right subiculum, right and left entorhinal cortex) when EPIs are acquired axially (arrow). All images in this figure are in radiological convention.
