Fig. 2.
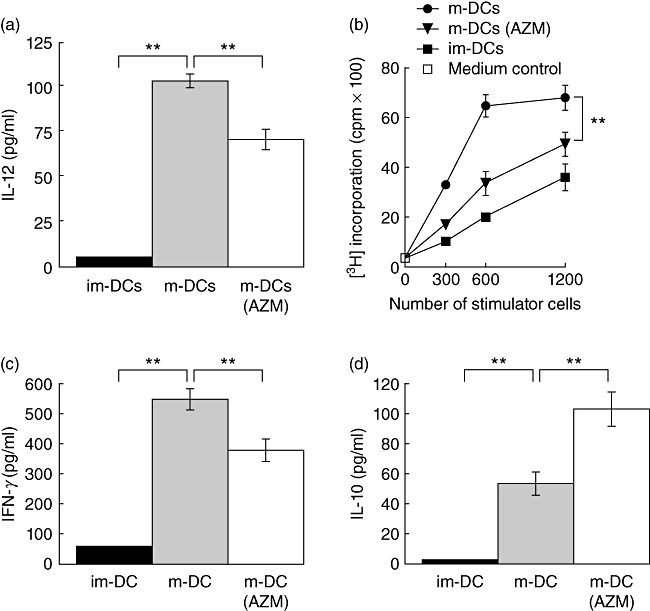
Azithromycin (AZM) inhibits dendritic cell (DC) functions. (a) AZM suppresses interleukin (IL)-12p70 production by DCs. AZM 50-treated (days 0, 3, 6) or untreated immature DCs (im-DCs) were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24 h. IL-12p70 concentration in the supernatants was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (b) AZM-treated mature DCs (m-DCs) inhibit their allogeneic CD4+ T lymphocyte stimulatory capacity in mixed leucocyte reaction (MLR). Irradiated bone marrow (BM)-derived control im-DCs, m-DCs or AZM 50-treated (days 0, 3, 6) m-DCs from BALB/c mice were used to stimulate 1 × 105 allogeneic splenic CD4+ T lymphocytes from C57BL/6 mice. The ability of DCs to stimulate allogeneic T lymphocytes was assessed by uptake of [3H]-thymidine. Interferon (IFN)-γ (c) or IL-10 (d) production measured by ELISA was decreased in the MLR supernatant. All results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate cultures. Data are representative of three independent experiments. **P < 0·001.
