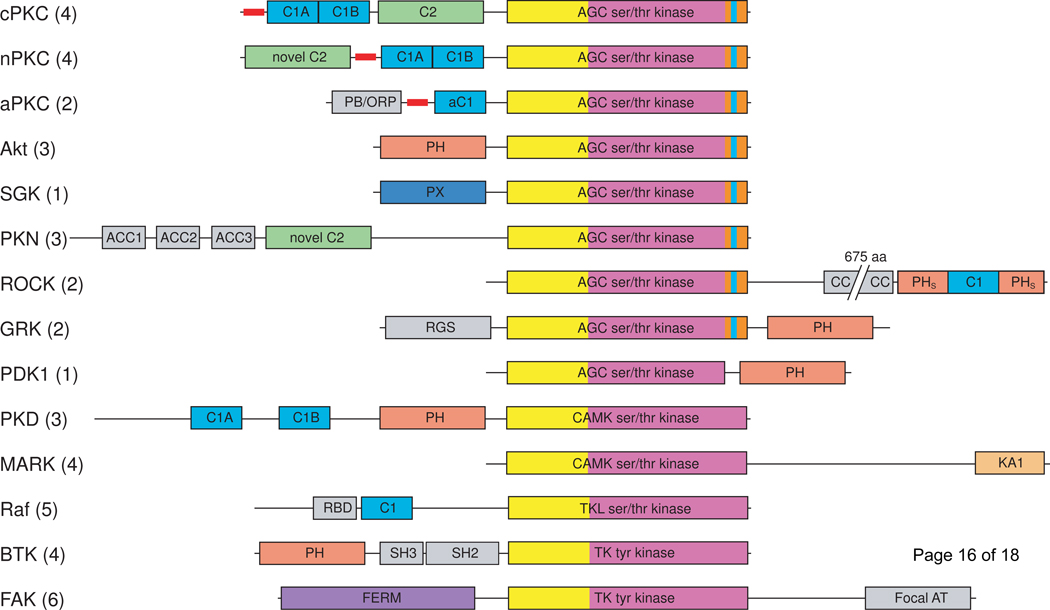
Figure 1.
Domain composition of the major protein kinase families containing lipid-binding domains. Lipid-binding domains are: C1 domain (light blue), C2 domain (green), PH domain (salmon), PX domain (dark blue), KA1 domain (pale orange), FERM domain (purple). The kinase domains are shown in yellow (N-lobe) and magenta (C-lobe); the AGC kinase family C-terminal tail is orange with the NFD motif highlighted in cyan. Pseudosubstrate segments are represented as thick red lines. Additional domains are shown in gray: Bem1 (PB/ORP), antiparallel coiled coil (ACC), coiled coil (CC), regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS), Ras binding domain (RBD), Src homology 2 (SH2). cPKC, conventional protein kinase C; nPKC, novel protein kinase C; aPKC, atypical protein kinase C; SGK, serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase; PKN, protein kinase N; ROCK, Rho-activated kinase; GRK, Gprotein coupled receptor kinase; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; PKD, protein kinase D; MARK, microtubule affinity regulating kinase; focal AT, focal adhesion targeting. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of mammalian kinases in each family.