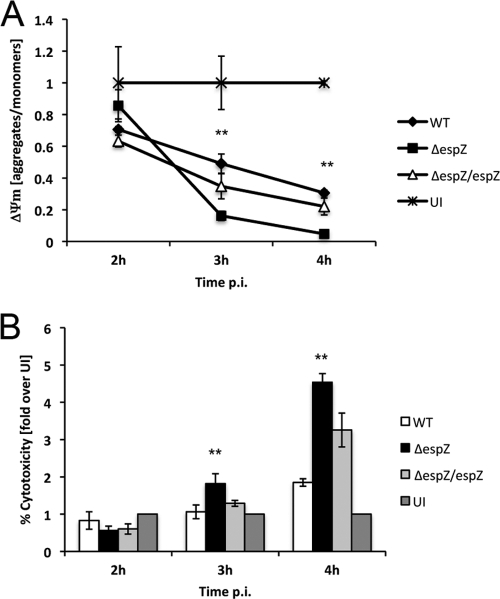
Fig. 2.
Infection with EPEC ΔespZ causes severe loss of Δψm. (A) HeLa cells were infected with either EPEC WT, ΔespZ, or ΔespZ/espZ or left uninfected (UI). JC-1 reagent was added to cells 15 min prior to termination of infection, and cells were washed with assay buffer three times. Fluorescence intensity was measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 560/595 nm and 485/535 nm for J monomers (low Δψm) and J aggregates (high Δψm), respectively. Δψm was plotted as the ratio of J aggregates/J monomers. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (P < 0.05) by Student's t test for samples tested in triplicate. p.i., postinfection. (B) Supernatants of HeLa cells infected for 2, 3, or 4 h with either EPEC WT, ΔespZ, or ΔespZ/espZ, left uninfected, or treated with Triton X-100 (100% cytotoxicity; data not shown) were assayed for the presence of LDH. Values were normalized against those for Triton X-100-treated cells (100% cytotoxicity) and uninfected cells (1% cytotoxicity). Asterisks indicate statistical significance (P < 0.05) by Student's t test for samples tested in triplicate. These data are representative of three independent experiments.