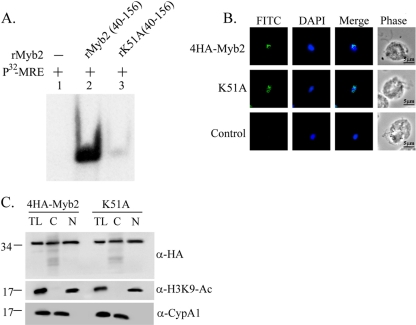
Fig. 8.
Effect of K51 on the DNA-binding activity and nuclear localization of Myb2. (A) A lysine residue, K51, in rMyb2(40∼156) (lane 2) was mutated to alanine to produce rK51A(40∼156) (lane 3). EMSA was performed with coincubation of the recombinant proteins with a γ-32P-labeled MRE-1 probe (lane 1). The reaction mixtures were separated in 12% gel. The signal was detected by autoradiogram. (B) The lysine residue, K51, in 4HA-Myb2 was mutated to alanine. Subcellular localization of 4HA-Myb2 and K51A was examined by IFA with a mouse anti-HA antibody. The signal was shown as green fluorescence (FITC). The nucleus was stained with DAPI, and cell morphology was recorded by phase-contrast microscopy. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Total lysates (TL) from cells overexpressing 4HA-Myb2 and K51A were fractionated into the nuclear (N) and cytosolic (C) fractions. Protein samples were separated in 12% gel for Western blotting with a rat anti-HA antibody (right panel). Duplicate blots were examined by using anti-acetyl-histone H3(Lys9) (α-H3K9-Ac) and anti-CypA1 (α-CypA1) antibodies.