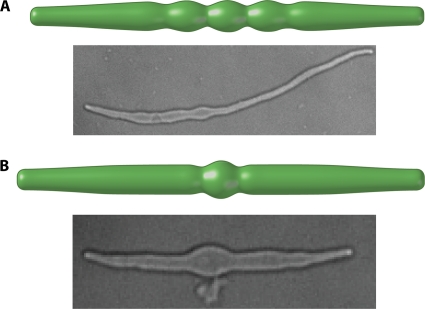
Fig. 7.
Growth-induced instability in bacterial cells. Mathematically computed cell shapes are compared with E. coli cells grown in a standard culture. The instability exhibits a characteristic wavelength, which for E. coli is about 5 μm. The cells are grown from an FtsZ deletion strain that carries a plasmid expressing a thermosensitive FtsZ (courtesy of the Margolin laboratory). Upon a temperature upshift, cells become filamentous, and A22 was added to disrupt MreB. The model predictions are similar to the wavelike bulges seen in these cells with disrupted MreB.