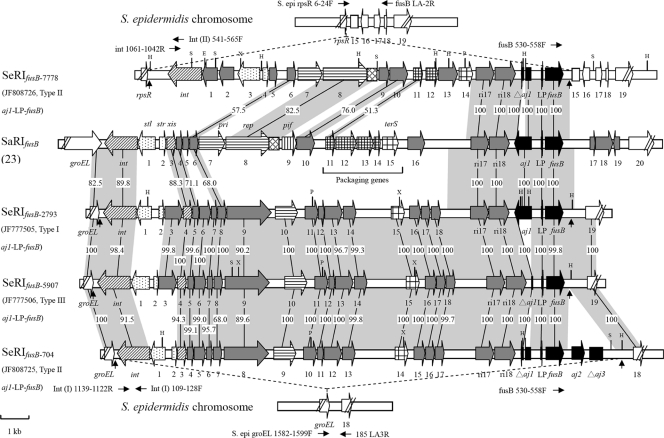
Fig. 1.
Genetic organization of SeRIfusB-2793 (GenBank accession no. JF777505), SeRIfusB-704 (GenBank accession no. JF808725), SeRIfusB-5907 (GenBank accession no. JF777506), and SeRIfusB-7778 (GenBank accession no. JF808726) compared with SaRIfusB (GenBank accession no. AM292600). Genes are drawn according to their sequences and function: int and xis are ; transcription regulators are ; replication genes (including the primase gene [pri] and the replication initiator gene [rep]) are ; the replication origin (ori) is ; of encapsidation genes, the terminase small subunit gene (terS) is and other genes are ; pif (phage interference) is ; aj1-LP-fusB regions are ; chromosome genes adjacent to SeRIfusB are ; other genes encoding hypothetical proteins are . The predicted direct repeats are indicated by vertical arrows. The horizontal arrows represent the PCR primers used to determine the insertion sites. Regions homologous between resistance islands are shown in shadow, and the numbers in shadow show percent homology between the corresponding sequences. The restriction sites are also shown: H, HindIII; P, PstI; X, XbaI; E, EcoRI; S, SpeI.