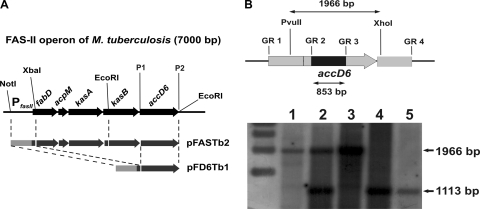
Fig. 2.
Complementation of the M. tuberculosis accD6 SCO strain. (A) Schematic demonstrating the construction of the complementation vectors that allowed us to replace the chromosomal copy of M. tuberculosis accD6 with its mutated copy. The dashed lines indicate the cloning steps, and the restriction sites are shown. P1 and P2 represent primers TBaccD6-XbaIs and TBaccD6-HindIIIrev, used to amplify the M. tuberculosis accD6 gene. (B) (Top) Map showing the length of the restriction DNA fragment (1,966 bp) and the internal deletion in the mutated gene (853 bp). The chromosomal localization of accD6 is represented by the gray arrow, while the internal deletion is marked by a black rectangle. (Bottom) Southern blot analysis confirming the deletion of the chromosomal copy of accD6 from complemented M. tuberculosis strains. Lanes represent genomic DNA from wild-type M. tuberculosis (lane 1), an SCO strain (lane 2), a DCO strain carrying the wild-type accD6 gene (wt-DCO) (lane 3), the ΔaccD6Mtb-PfasII-acc D6Mtb mutant (lane 4), and the ΔaccD6Mtb-PfasII-FASIIMtb mutant (lane 5).