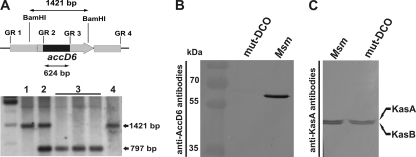
Fig. 3.
Confirmation of the loss of a functional accD6 gene in the M. smegmatis ΔaccD6 DCO mutant. (A) (Top) Schematic showing the restriction-digested DNA fragment (1,421 bp) and the size of the internal deletion in the mutated gene (624 bp). The accD6 gene is represented by the gray arrow and the internal deletion by a black rectangle. (Bottom) Southern blot confirming the deletion of accD6 in mutated M. smegmatis. Lanes: 1, wild-type M. smegmatis; 2, single-crossover strain; 3, double-crossover ΔaccD6 mutant; 4, wild-type DCO strain. (B) Western blot of total crude lysates from M. smegmatis (Msm) and a ΔaccD6 DCO mutant (mut-DCO) strain confirming the loss of AccD6 protein expression in the mutant strain, as assessed using rabbit anti-AccD6 antibodies. (C) Western blot of total crude lysates from M. smegmatis and mut-DCO strains confirming that the protein expression levels of KasA and KasB were similar in the wild-type and mutant strains, as assessed using rat anti-KasA antibodies capable of cross-reacting with KasB.