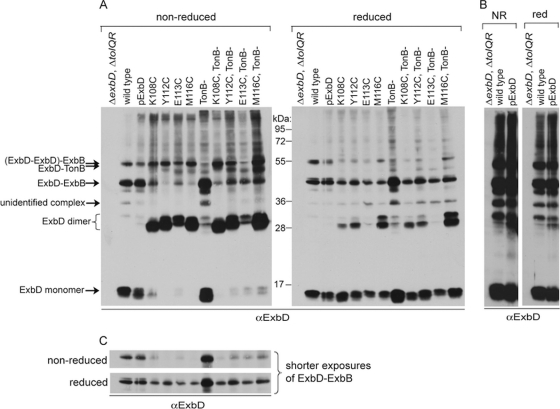
Fig. 4.
ExbD disulfide-linked homodimers assemble with ExbB. Strains expressing chromosomally encoded wild-type ExbD (W3110) in the absence of TonB (KP1344) or a ΔexbD ΔtolQR strain (RA1045) or a ΔexbD ΔtolQR ΔtonB (KP1509) strain expressing plasmid-encoded wild-type ExbD (pExbD) or ExbD Cys substitutions near native ExbD levels (see Table S1 in the supplemental material for induction levels) were treated with CuoP, washed, and then cross-linked with formaldehyde as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Samples were resolved on 13% nonreducing or reducing SDS-polyacrylamide gels and immunoblotted with ExbD-specific polyclonal antibodies. The positions of monomeric ExbD and ExbD-specific cross-linked complexes are indicated on the left. The positions of molecular mass standards are indicated between the immunoblots. (B) Long exposures of the immunoblots in panel A showing only the strains expressing wild-type ExbD. NR indicates nonreduced. Red indicates reduced. (C) Short exposures of the immunoblots in panel A, cropped to the region of the ExbB-ExbD heterodimer, are shown for better comparison of relative levels of the complex under nonreducing or reducing conditions.