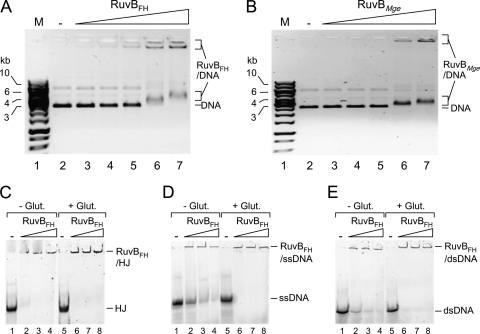
Fig. 2.
DNA-binding activity of RuvBFH and RuvBMge. (A) Binding of RuvBFH to supercoiled plasmid DNA. The DNA-binding reactions were performed as indicated in Materials and Methods. In short, reactions were performed in volumes of 10 μl and contained 20 ng of DNA, 1 mM ATPγS, and either 0 nM (−; lane 2), 340 nM (lane 3), 680 nM (lane 4), 1.35 μM (lane 5), 2.7 μM (lane 6), or 5.4 μM (lane 7) RuvBFH. The protein-DNA mixtures were separated by native 0.6% agarose gel electrophoresis, followed by staining with ethidium bromide. A black/white inverted image of the stained gel is shown. The positions of the unbound DNA (DNA) and RuvBFH-DNA complexes are indicated at the right-hand side of the gel. The sizes of DNA marker fragments (M, lane 1; SmartLadder [Eurogentec]) are shown on the left-hand side of the gel in kb. (B) Binding of RuvBMge to supercoiled plasmid DNA. Reactions were performed and analyzed using a method similar to that described for panel A and contained either 0 nM (−; lane 2), 340 nM (lane 3), 680 nM (lane 4), 1.35 μM (lane 5), 2.7 μM (lane 6), or 5.4 μM (lane 7) of RuvBMge. (C) Binding of RuvBFH to (6-FAM-labeled) HJ substrate HJ1.1 (33). Reactions were performed using a method similar to that described for panel A and contained either 0 nM (−; lanes 1 and 5), 1.35 μM (lanes 2 and 6), 2.7 μM (lanes 3 and 7), or 5.4 μM (lanes 4 and 8) of RuvBFH. The reaction products were separated on a 5% polyacrylamide gel and analyzed by fluorometry. The reactions shown in lanes 5 to 8 (+Glut.) were treated with 0.25% glutaraldehyde (30 min at 37°C) after the binding reactions. The reactions shown in lanes 1 to 4 were not treated with glutaraldehyde (−Glut.) (D) Binding of RuvBFH to ssDNA (5′ 6-FAM-labeled oligonucleotide 1) (Fig. 3A). Reactions were performed using a method similar to that described in panel C. (E) Binding of RuvBFH to dsDNA (substrate VI; 5′ 6-FAM labeled on oligonucleotide 2/1) (Fig. 3A). Reactions were performed using a method similar to that described in panel C.