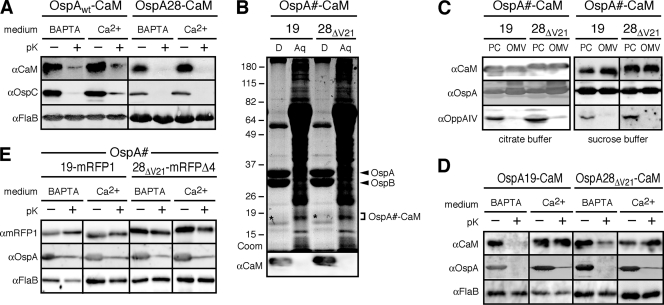
Fig. 3.
Chelation-dependent surface exposure of OspA-CaM fusion proteins at steady state. (A) Accessibility of full-length OspA-CaM or OspA tether-CaM fusion proteins to proteinase K. Cells expressing the fusion constructs were grown in BSK-SFcc containing either Ca2+ or BAPTA. Lipoprotein surface exposure was assessed by incubating intact cells with proteinase K (pK+) or a control buffer (pK−), followed by Western immunoblotting with antibodies against CaM, OspC (used as an OspA-independent surface control, due to the coexpression of endogenous OspAwt and OspAwt-CaM), and FlaB (periplasmic control) (αCaM, αOspC, and αFlaB, respectively). (B) Total-protein fractionation by Triton X-114 of B. burgdorferi cells expressing the OspA28ΔV21-CaM or OspA19-CaM fusion protein in the presence of Ca2+. A Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel (Coom) and an immunoblot with αCaM are shown. D, detergent phase; Aq, aqueous phase. The positions of OspA and OspB are indicated on the right. Asterisks indicate the weakly Coomassie stained OspA-CaM fusion bands present in the respective detergent fractions. (C) Membrane fractionation immunoblots of the subsurface OspAΔV21-CaM and OspA19-CaM fusion proteins expressed by B. burgdorferi in the presence of Ca2+. OppAIV served as an inner membrane control, and OspA served as an OM control. PC, protoplasmic cylinder fraction; OMV, outer membrane vesicle fraction enriched for OM proteins. Note that the PC fraction also contains OM proteins, because OMVs were only partially separated from protoplasmic cylinders by treatment of Borrelia cells with a hypotonic citrate buffer; therefore, the PC fraction is similar to a whole-cell protein preparation (54). (D) Accessibility to proteinase K of partial or mutant OspA tether-CaM fusion proteins expressed by B. burgdorferi. The experimental procedures and labels described for panel A were used, except that OspA was used as the standard surface control. (E) Accessibility to proteinase K of previously described periplasmic OspA-mRFP fusion proteins (50, 51) under calcium-containing (Ca2+) or chelating (BAPTA) conditions. The experimental procedures and labels were the same as those for panel D.