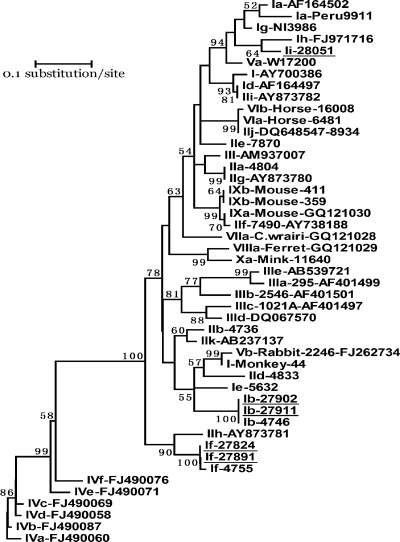
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic relationship of gp60 nucleotide sequences of Cryptosporidium hominis in this study and known Cryptosporidium subtype families, as inferred by a neighbor-joining analysis (Mega 4 software [http://www.megasoftware.net/]) based on genetic distances calculated using the Kimura two-parameter model. Bootstrap values greater than 50% from 1,000 pseudoreplicates are shown. The gp60 tree was rooted with GenBank sequence FJ490060. The name of each subtype family starts with the Cryptosporidium species or genotype designation, with C. hominis, Cryptosporidium parvum, Cryptosporidium meleagridis, Cryptosporidium fayeri, C. cuniculus, horse genotype, Cryptosporidium wrairi, ferret genotype, and mouse genotype I represented by I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, and IX, respectively. Ii near the top of the tree is a new C. hominis subtype family found in this study. Subtype families seen in baboons in this study are underlined.