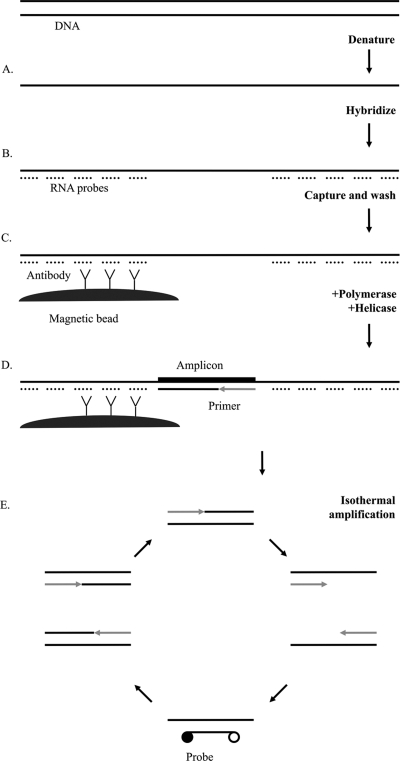
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the tHDA assay for detection of C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae. (A) Samples are lysed, and DNA is denatured. (B) RNA probes are hybridized. (C) RNA-DNA hybrids are captured on a monoclonal hybrid capture antibody conjugated to magnetic beads. (D) tHDA reagents are added to washed beads. (E) DNA polymerase extends primers hybridized to single-stranded DNA. UvrD helicase unwinds the double-stranded DNA for the next round of amplification. Exponential amplification occurs through continuous isothermal (65°C) activity of the helicase and polymerase. Hybridization of fluorescent-labeled probes generates a signal.