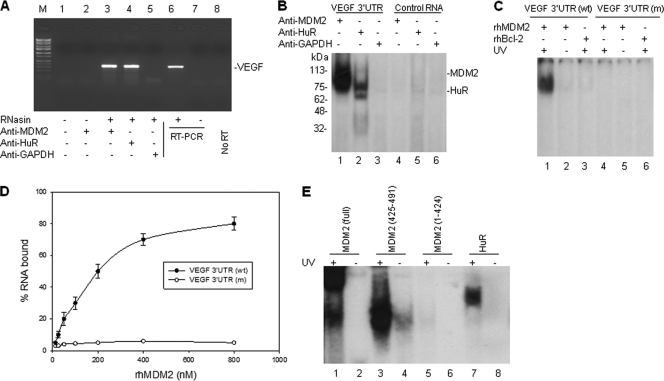
Fig. 3.
MDM2 protein binds to VEGF mRNA in vivo and in vitro. (A) Cell extracts from NB-1691 cells were prepared in RNA binding buffer in the presence of RNase inhibitor (RNasin). Following coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) with anti-MDM2, anti-HuR (positive control), and anti-GAPDH (negative control), VEGF mRNA was detected by RT-PCR analysis. The positive control (NB-1691 total RNA as the template) (lane 6), negative control (no template) (lane 7), and no RT (lane 8) controls for RT-PCR are also shown. Lane M contains molecular size markers. (B) Cellular extracts from NB-1691 were incubated with 32P-labeled RNA probes corresponding to the VEGF 3′UTR and a control RNA, next UV cross-linked, and then immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies. These protein-RNA probe complexes were run on an SDS-polyacrylamide gel and imaged by autoradiography. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown to the left of the gel. (C) The rhMDM2 and rhBcl-2 (control) proteins were incubated with 32P-labeled normal VEGF 3′UTR and ARE-mutated (m) VEGF 3′UTR, respectively. The protein-RNA complexes were detected as described above for panel B. (D) Filter binding assay showing the binding of rhMDM2 to VEGF 3′UTR. The means ± standard deviations (error bars) (SD) of the results from three independent experiments are shown. (E) GST-fused full-length MDM2, different GST-fused MDM2 fragments of the C-terminal RING domain (positions 425 to 491), a MDM2 fragment with a deletion of the C-terminal RING domain (positions 1 to 424), and the GST-fused HuR control were incubated with 32P-labeled VEGF 3′UTR. Formation of any MDM2-VEGF RNA complexes were detected as described above for panel B.