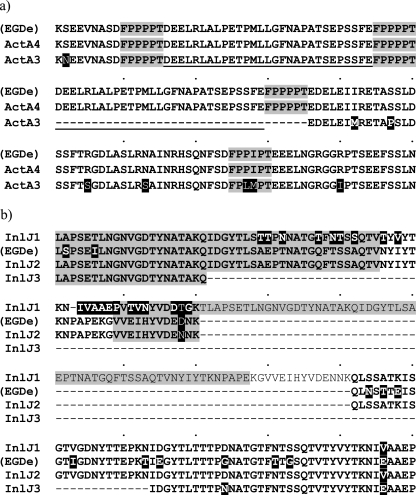
Fig. 3.
(a) Alignment of the nucleotide sequence-derived amino acid sequences of the variable parts of ActA for the two different actA alleles. PRRs are marked in gray. The dashes indicate the 35 amino acids missing in ActA3, consisting of the 29 amino acids from the long repeat (underlined) and one 6-amino-acid-long PPR marked in gray. L86 (ActA4) and L11 (ActA3) predicted amino acid sequences are compared to ActA of the EGDe strain (accession number CAA42407). The amino acid variations in ActA3 are indicated by the black background. (b) Alignment of the nucleotide sequence-derived amino acid sequences of the variable part of InlJ for the three inlJ alleles. The predicted amino acid sequences of InlJ1, InlJ2, and InlJ3 are compared to InlJ of strain EGDe (accession number NP_466343). The dashes indicate the missing amino acids. The amino acid variations are indicated with a black background. Amino acids belonging to mucin-binding protein (MucBP) domains are marked in gray.