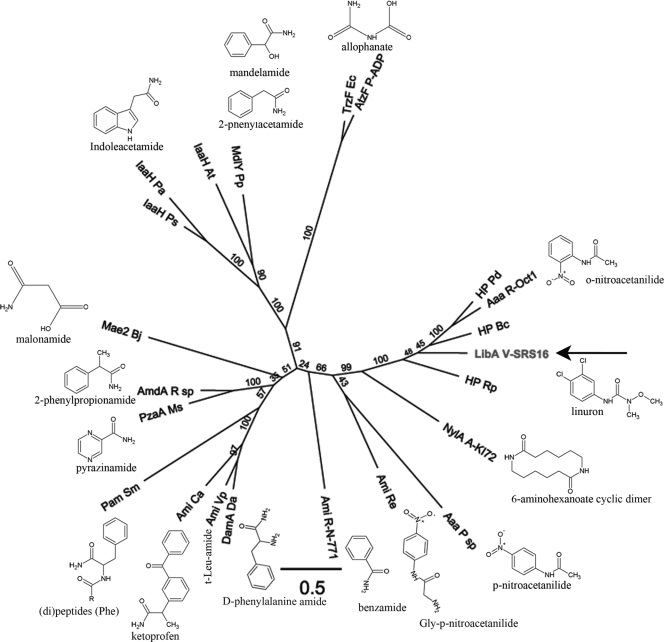
Fig. 5.
Phylogenetic analysis of LibA and selected members of the amidase signature family. A multiple amino acid alignment of the respective Pfam domains (PF01425) was used to construct a maximum-likelihood tree. The AS domain of LibA (residues 27 to 453) was aligned with the corresponding domain of the following enzymes, with their (preferred) substrates indicated: Aaa R-Oct1 (Rhodococcus sp. strain Oct1, o-nitroacetanilide [15]), Aaa P sp (Pseudomonas sp., p-nitroacetanilide [24]), AmdA R sp (Rhodococcus sp., 2-phenylpropionamide [28]), Ami Ca (Comamonas acidovorans, ketoprofen [58]), Ami Re (Rhodococcus erythropolis PR4, Gly-p-nitroacetanilide [26]), Ami R-N-771 (Rhodococcus sp. strain N-771, benzamide [32]), Ami Vp (Variovorax paradoxus, t-Leu-amide [25]), AtzF P-ADP (Pseudomonas sp. ADP, allophanate [43]), DamA Da (Delftia acidovorans, d-phenylalanine amide [22]), IaaH At (Agrobacterium tumefaciens, indole acetamide [57]), IaaH Pa (Pantoea agglomerans, indole acetamide [8]), IaaH Ps (Pseudomonas savastanoi, indole acetamide [57]), Mae2 Bj (Bradyrhizobium japonicum, malonamide [45]), MdlY Pp (Pseudomonas putida, mandelamide/2-phenylacetamide [17]), NylA (Arthrobacter sp. strain KI72, 6-aminohexanoate cyclic dimer/β-laurolactam [59]), Pam Sm (Stenotrophomonas maltophila, [di]peptides [Phe] [30]), PzaA Ms (Mycobacterium smegmatis, pyrazinamide [4]), and TrzF Ec (Enterobacter cloacae, allophanate [42]). Three hypothetical proteins most similar to LibA were included: HP Bc (Burkholderia cenocepacia J2315 [YP_002234156]), HP Pd (Pseudonocardia dioxanivorans [YP_004335959]), HP Rp (Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3 [YP_167742]). The scale bar represents 0.5 substitutions per site. Bootstrap values are represented at the branches.