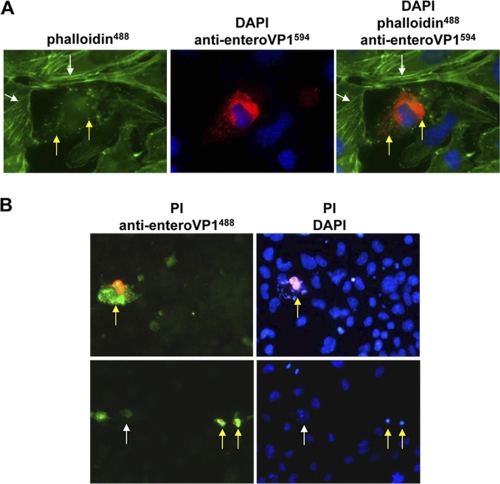
Fig. 2.
Pathogenic alterations caused by CVB3 infection in the persistently infected HL-1CVB3 cell line. (A) Disruption of cytoskeleton in CVB3-infected HL-1CVB3 cells. Cells were stained for detection of CVB3 VP1 expression as described for Fig. 1A. Staining of F-actin filaments was carried out with Alexa-Fluor488 (green)-conjugated phalloidin. CVB3-infected cells in the culture showed disruption of actin filaments and accumulation of actin conglomerates (green spots and yellow arrows), whereas uninfected cells showed intact filamentous actin fibers (white arrows). Magnification, 1,000-fold. (B) Detection of cytopathic effect in CVB3-infected HL-1CVB3 cells. CVB3-infected cells were incubated with propidium iodide (PI) (red) and then stained with enterovirus-specific VP1 antibody and a secondary antibody conjugated with Alexa-Fluor488 (green) (left panels) and then with DAPI (blue) (right panels). Red-green and magenta-blue costaining reveals CVB3-infected dead cells (yellow arrows), whereas cells stained solely green (white arrow, lower left panel) may represent CVB3-infected cells at an early replication stage without signs of cell death. Magnification, 400-fold.