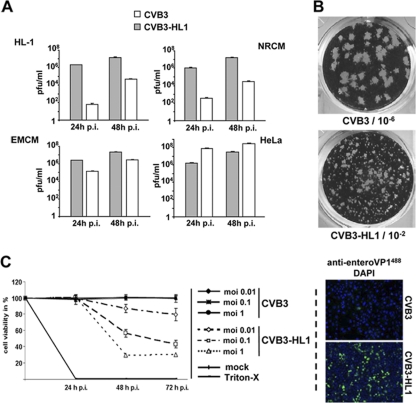
Fig. 3.
Alteration of infectivity and replication activity of CVB3-HL1. (A) Replication of CVB3-HL1 in cardiac and HeLa cells in vitro. HeLa cells, native HL-1 cells, NRCM, and EMCM were infected with CVB3 and CVB3-HL1 at an MOI of 0.1. Plaque assays were performed 24 and 48 h later. In comparison to CVB3, CVB3-HL1 showed distinctly increased replication in the cardiac cell lines but lower replication in HeLa cells. Values are given as means ± standard deviations (SD) of the results of two independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. p.i., postinfection. (B) Representative plaque assay of CVB3 (dilution, 10−6) and CVB3-HL1 (dilution, 10−2) in HeLa cells. The CVB3-HL1 variant showed a smaller plaque size than CVB3. (C) Infectivity of CVB3-HL1 versus CVB3 in HL-1 cells. (Left panel) HL-1 cells were seeded in 96-well plates and infected with different doses of CVB3 and CVB3-HL1. Cell viability was measured by cell proliferation assays performed with uninfected cells (mock) as a control (set as 100%). CVB3-HL1, but not CVB3, induced cell lysis in HL-1 cells. Values are given as means ± SD of the results of two experiments, each performed in quadruplicate. (Right panel) HL-1 cells were infected with CVB3 and CVB3-HL1 at an MOI of 1. VP1 capsid protein was detected by immunofluorescence using an anti-enterovirus VP1 antibody (green) 24 h later. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Magnification, 100-fold. Compared to CVB3 infection, CVB3-HL1 infection showed a drastic increase in the number of VP1-positive HL-1 cells.