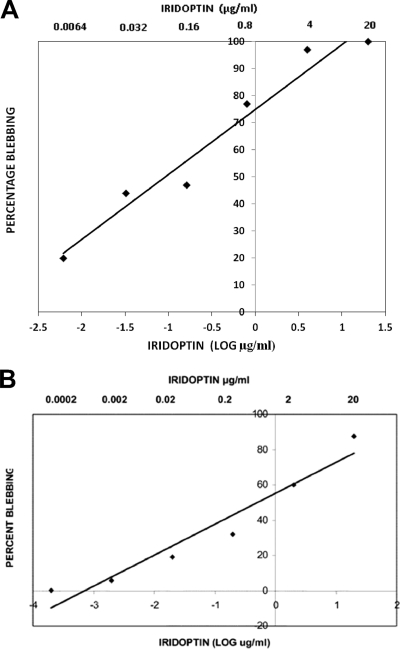
Fig. 5.
Dose-response analysis of iridoptin-induced apoptosis in budworm and boll weevil cells. (A) Budworm cells (CF) were treated with dilutions of iridoptin starting at 20 μg/ml (final concentration) and incubated at 28°C for 24 h. Cells were observed for apoptotic blebs with a phase-contrast microscope. Percent blebbing was determined from approximately 250 cells per field. Linear regression line and R2 value were generated using Microsoft Excel 2003. The linear regression line was generated with the following equation: y = 24x + 75, where x is the log of final iridoptin concentration in μg/ml and y is the percentage of cell population with blebs. The R2 value for the fitted line was 0.95. The highest dilution of toxin-produced blebbing in 50% of the cell population was approximately 0.1 μg/ml. (B) Boll weevil (AG) cells. The line was generated by the following equation: y = 17.5x + 55, where x is the log of final iridoptin concentration in μg/ml and y is the percentage of cell population with blebs. The R2 value for the fitted line was 0.94. The final concentration of iridoptin required to induce blebbing in 50% of the cell population was 0.5 μg/ml. Assays for both cell lines were performed in triplicate.