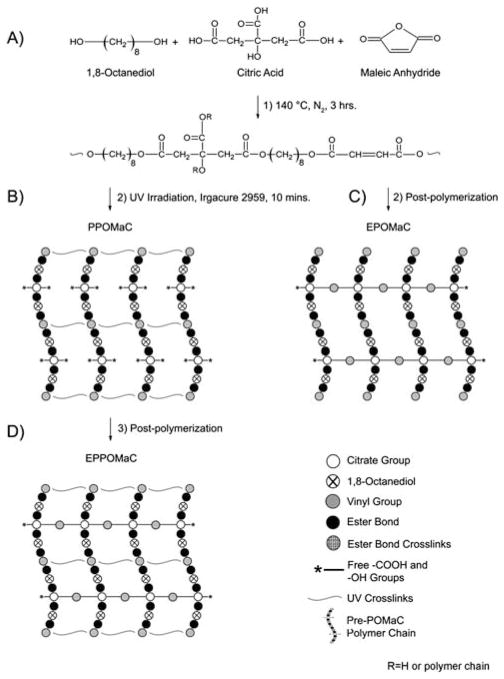
Fig. 1.
A schematic representation of POMaC synthesis, networks, and dual crosslinking mechanism. (A) The monomers 1,8-octanediol, citric acid, and maleic anhydride underwent condensation polymerization to produce pre-POMaC with successful incorporation of vinyl carbons and degradable ester bonds located throughout the polymer backbone. (B) Upon exposure to UV irradiation, the free radical polymerization is initiated to crosslink pre-POMaC through the vinyl carrying carbons to yield photocrosslinked POMaC (PPOMaC). Notice the available free carboxylic acid and hydroxyl functional groups remaining from citric acid after photocrosslinking. (C) Pre-POMaC can also be crosslinked through polycondensation without photocrosslinking to obtain ester bond crosslinked POMaC (EPOMaC). (D) Post-polymerization can be used to further crosslink PPOMaC through the available free functional groups of citric acid to yield ester bond crosslinked photocrosslinked POMaC (EPPOMaC).