Figure 1.
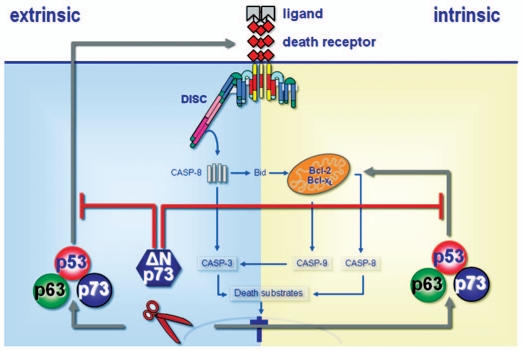
Model summarizing the work of Schuster el al. which argues for an oncogenic role of ΔNp73 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Upon DNA damage, TAp73, like p53, engages the major apoptosis pathways in the cell, death receptors and mitochondria, via transcription-dependent mechanisms.6 On the contrary, ΔNp73 confers apoptosis- and drug-resistance by inhibition of both pathways. These data suggest that the ratio TAp73/ΔNp73 regulates the apoptotic response of cancer cells following treatment with DNA damaging agents thereby playing a decisive role for treatment sensitivity versus drug resistance. Of clinical relevance, the authors show that the ΔNp73 target gene signature is a predictor of adverse outcome in patients with HCC and establish ΔNp73 as a prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma.