Figure 1.
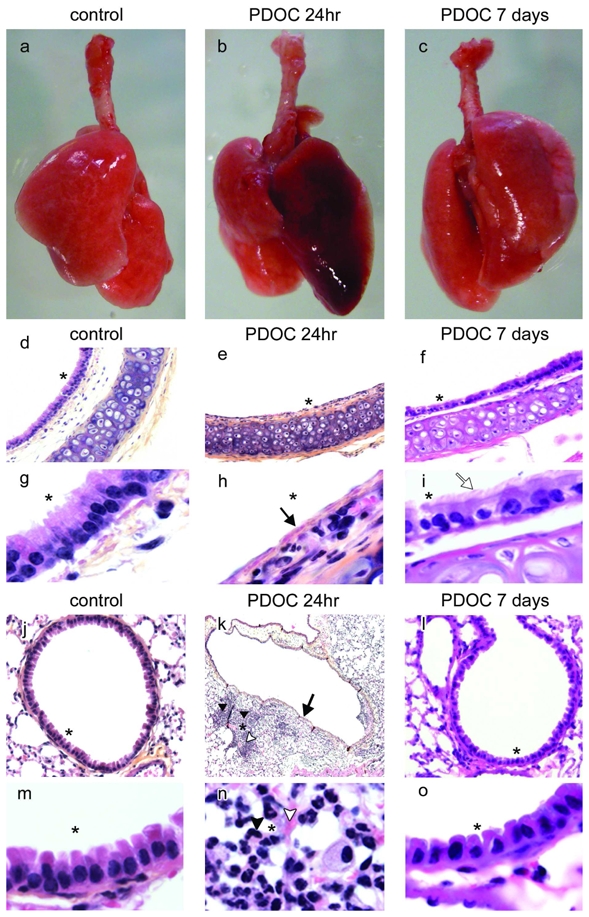
Epithelial damage induced by intratracheal administration of polidocanol (PDOC). (a–c) Trachea-lungs from (a) control animal, (b) animals injected with PDOC at 24hr and (c) 7 days after PDOC administration. (d–i) tracheal and (j–o) bronchial sections from (d,g,j,m) control animal, (e,h,k,n) animals injected with PDOC at 24hr and (f,i,l,o) at 7 days. (k) Magnification 4x. (d–f) Magnification 10x. (j,l) Magnification 20x. (g–i,m–o) Magnification 100x. Haematoxylin counterstaining, airway epithelial damage (arrows), ciliated cells (white arrow), inflammation areas (arrow heads), haemorrhagic areas (white arrow heads). Areas marked by asterisks were magnified in the adjacent pictures.
