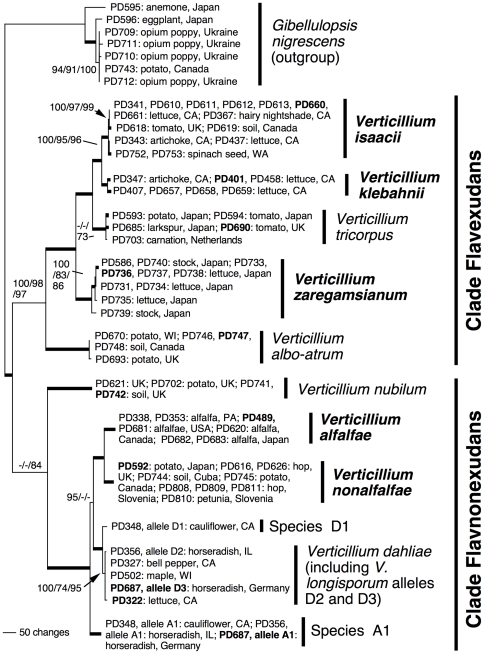
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationship of the ten Verticillium species based on the combined ACT, EF, GPD and TS dataset of 2658 characters and 77 taxa, with Gibellulopsis nigrescens as outgroup.
The Bayesian consensus tree is shown. Isolates are represented by their unique PD identifiers followed by host and geographic origin, PD identifiers in bold represent ex-type strains. Species are marked by vertical bars followed by species names, species in bold were described in this study. The two main clades recovered are indicated on the right. Numbers by the branches are Bayesian, likelihood and parsimony support values above 70 in that order, branches in bold had maximal support in all analyses. For the diploid hybrid V. longisporum, allele designations are also given following PD identifiers. Each isolate of V. longisporum has two alleles that are present in two different clades in the tree, in hypothetical Species A1, and either in hypothetical Species D1 or in V. dahliae, reflecting the hybrid origin of this species [27]. Groupings not visible in the tree but still receiving support include the clade of strains PD710 and PD743 with 71% bootstrap support, the clade of strains PD356, PD327 and PD502, with 100%, 78% and 73% Bayesian, likelihood and parsimony support, respectively; the clade of strains PD709 and PD711 and the clade of strains PD710 and PD743 with respectively 84 and 98% of the Bayesian posterior probabilities.