Table 1.
Discovery of the intermolecular oxidative aminatio[a]
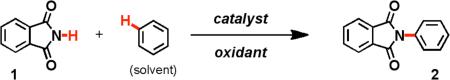 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidant (equiv) | Solvent | Temp. [°C] | Time [h] | Yield [%][c] | |
| 1 | PIDA (1.5) | PhH | 145[b] | 12 | 26 |
| 2 | PIDA (1.5) | PhH | 145 | 3 | 28 |
| 3 | PIDA (2.0) | PhH | 145 | 3 | 45 |
| 4 | PIDA (2.5) | PhH | 145 | 3 | 88 |
| 5 | PIDA (2.5) | PhH | 120 | 3 | no reaction |
| 6 | PIDA (2.5) | TFE | 145 | 3 | 13 |
| 7 | PIDA (2.5) | DMF | 145 | 3 | 4[d] |
| 8 | PIDA (2.5) | DMSO | 145 | 3 | no reaction |
| 9 | PIDA (2.5) | MeCN | 145 | 3 | 51 |
| 10 | NCS (2.5) | MeCN | 145 | 3 | 3[d] |
| 11 | Oxone (2.5) | MeCN | 145 | 3 | no reaction |
| 12 | IBX (2.5) | MeCN | 145 | 3 | no reaction |
| 13 | PIFA (1.0) | PhH | 145 | 3 | 5[d] |
| 14 | PIFA (1.25) | PhH | 145 | 3 | decomposition |
| 15 | PIFA (1.0) | PhH | 100 | 3 | Trace |
| 16 | PIFA (1.0) | PhH | 25[b] | 3 | 0 |
| 17 | PIFA (1.0) | TFE | 145 | 3 | 3.5[d] |
| 18 | PIFA (1.0) | MeCN | 145 | 3 | 3.5[d] |
General reaction conditions: 1 (0.68 mmol), oxidant (1.5 - 2.5 equiv), benzene (1.5 equiv or solvent), solvent (4 mL), microwave heating. PIDA = phenyliodine(III) diacetate, PIFA = phenyliodine(III) bis(trifluoroacetate), NCS = N-chlorosuccinimide, IBX = 2-iodoxybenzoic acid, Oxone = potassium peroxymonosulfate, TFE = 2,2,2-trifluoro-ethanol.
Oil bath.
Yield of isolated product after column chromatography.
GC yield calculated using dodecane as internal standard.
