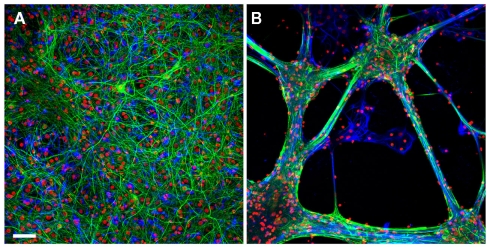
Figure A1.
The growth pattern of the hippocampal cells on poly-d-lysine/laminin versus EPP. Retrospective immunolabeling of 20 days old hippocampal cells grown on poly-d-lysine (A) and EPP (B): neurons (green), glial cells (blue), counterstained with nuclear marker DAPI (red). Scale bar: 50 μm. Neurons were labeled for neuron-specific intermediate filaments with mouse anti NF antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies conjugated to Cyanine 2 (Cy2). Glial cells were labeled for glial fibrillary acidic proteins with primary anti-GFAP rabbit monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies conjugated to Cy3. Confocal imaging was done using D-Eclipse C1 imaging system (Nikon) mounted on an Eclipse TE-2000 microscope (Nikon). Images were collected and processed using EZ-C1 software (Nikon). Scanning was done in sequential mode: red was excited with 543 nm He–Ne laser and collected with 605 ± 75 band pass filter; green was excited with 488 nm Argon laser and collected with 515 ± 30 band pass filter; blue excited with 405 nm Diode and collected with 450 ± 35 band pass filter. Images were prepared using the open-source image analysis program ImageJ (NIH, USA). Hippocampal cells grown on the EPP clustered to form bundles and aggregates in which the glia cells formed a sheet in contact with the substrate and the neurons grew on top. Cells in different aggregates interconnect by thick fascicles emanating from clusters and projecting to adjacent aggregates.