Figure 5. Post-revision T cells undergo rapid proliferation to bacterial Ag following transfer into chronically lymphopenic recipients.
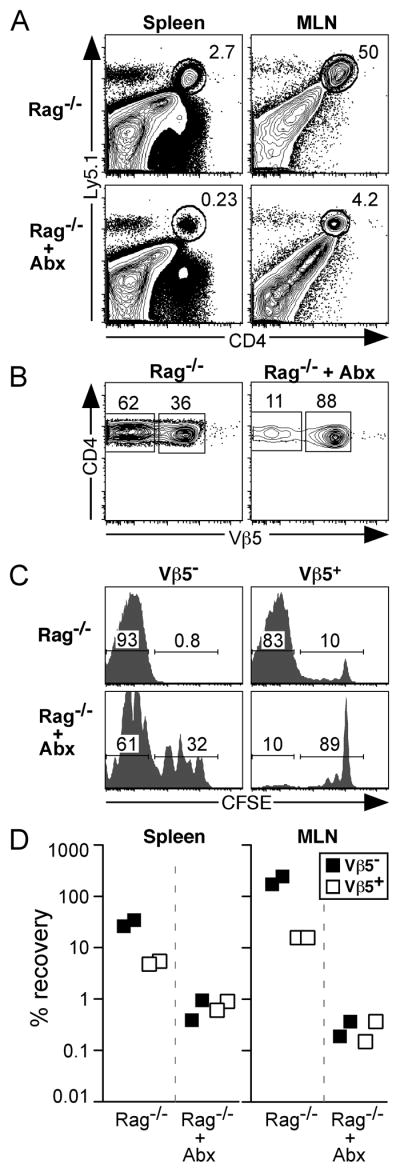
2.6×106 CFSE-labeled Ly5.1+ CD4+ T cells (comprised of 12% Vβ5− post-revision cells and 88% Vβ5+ cells) enriched from pooled spleen and lymph nodes of aged Vβ5 Tg mice were transferred into chronically lymphopenic Rag−/− recipient mice that were either untreated or treated (+ Abx) with a cocktail of antibiotics in their drinking water beginning 6 days prior to adoptive transfer. Donor CD4+ T cells were analyzed 6 days post-transfer for the extent of proliferation as measured by CFSE dilution and the percent recovery of each population. A. Analysis of live gated splenocytes and MLN cells with gate indicating Ly5.1+ donor CD4+ T cells. B. CD4 and Vβ5 analysis of donor Ly5.1+CD4+ gated cells from the MLN. C. CFSE analysis of donor CD4+Vβ5− (left) and CD4+Vβ5+ (right) T cells from the MLN. Numbers within CFSE histograms represent the percent of gated cells that have fully diluted CFSE (left), or have undergone 0–4 cell divisions (right). D. Charts indicate the percent recovery of donor Vβ5− and Vβ5+ CD4+ T cells in spleen and MLN.
