Figure 1.
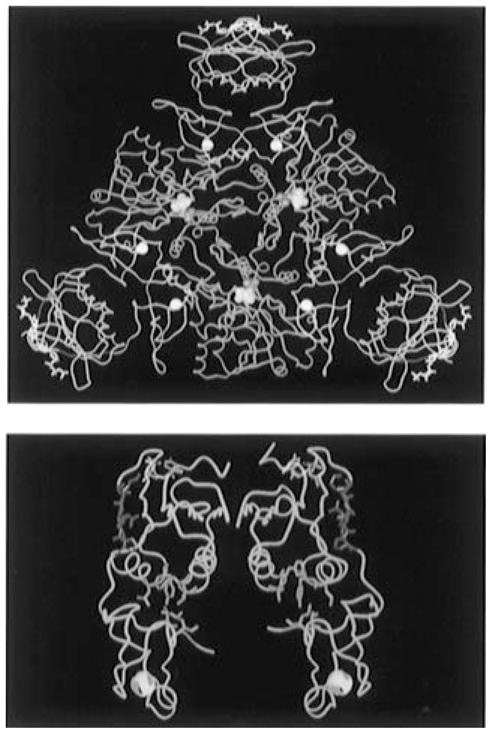
(A, top) Molecular graphic representation of a CTP-liganded R-state holoenzyme of ATCase from Ec. The holoenzyme is composed of two catalytic trimers (one trimer is shown in blue while the second is located beneath this trimer and not shown here for the purpose of simplication) and three regulatory dimers (in yellow). The nucleotide effector CTP (in white sticks and purple balls) binds on the allosteric domain and exerts its effect through the zinc domain (six zinc atoms are indicated as white balls) to the catalytic sites 60 Å away [the catalytic site lies between the Asp and CP domains of each catalytic monomer and is defined by the substrate analogs phosphonoacetamide (purple balls) and malonate (yellow balls)]. The substituted regions (r93–r97, red ribbon) are located at the junction between the allosteric binding sites and the catalytic sites. (B, bottom) The α-Carbon trace of a regulatory dimer is shown in yellow. The altered S5′ β-strand regions (r93–r97) are shown in red; the CTP nucleotide effectors in purple occupy the allosteric binding site; and the hydrophobic pockets (green) are located at the interface of the allosteric and zinc domains. All atomic coordinates are originally from file “8at1.full” in the Protein Data Bank supplied by Gouaux et al. (1990).
