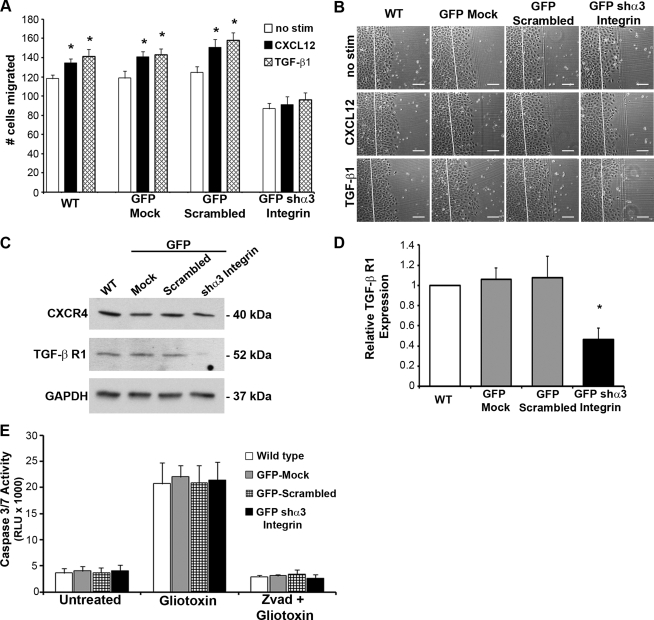
Fig. 7.
Depletion of α3-integrin prevents inducible cell restitution. A: migration-inducing stimulants CXCL12 (2.5 nM) (solid bars) or transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 (5 ng/ml) (hatched bars) were unable to increase migration of GFP-shα3 integrin-depleted IEC-6 cells. Control WT, GFP-Mock, and GFP-Scrambled control transduced cells had significant induction of migration by both CXCL12 and TGF-β1 compared with unstimulated (open bars) controls. Data are means ± SE of 9 individual experiments. B: representative photomicrographs of WT, GFP-Mock, GFP-Scrambled, and GFP-shα3 integrin IEC-6 cells stimulated with CXCL12, TGF-β1, or left untreated (no stim). Scale bar = 125 μm. C: representative immunoblots show depletion of TGF-β receptor 1 (TGFβR1), whereas CXCR4 levels were unaffected by α3-integrin depletion. D: densitometric quantification of TGFβR1 in WT (open bar), GFP-Mock, GFP-scrambled (shaded bars), and GFP-shα3 integrin (solid bar) IEC-6 cells confirmed significant depletion of TGFβR1 in GFP-shα3 integrin cells. Data are expressed as relative TGFβR1 levels normalized to the GAPDH loading control from 7 different immunoblot analyses. Asterisk denotes statistically significant difference from WT cells (*P ≤ 0.05). E: caspase 3/7 activity in WT, GFP-Mock, GFP-scrambled, and GFP-shα3 integrin IEC-6 cells was assessed using a luciferase-based assay. Gliotoxin (2 μg/ml) treatment was used to induce cell death, whereas zVAD (10 μg/ml), a pan-caspase inhibitor, confirmed that gliotoxin-induced cell death was the result of caspase activity. Values are means ± SE of 3 individual experiments.