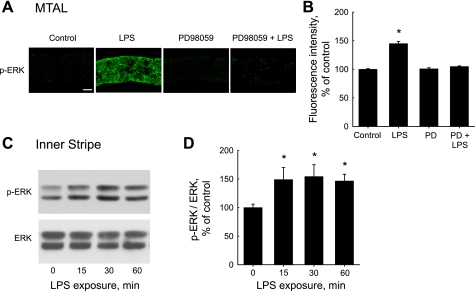
Fig. 2.
LPS increases ERK phosphorylation in the MTAL. A: MTALs dissected from rats were incubated in vitro at 37°C in control solution, LPS (500 ng/ml), PD98059 (15 μM), or PD98059 + LPS for 15 min and then fixed and stained with antiphospho-ERK1/2-Thr202/Tyr204 (p-ERK) antibody. The tubules were analyzed by confocal immunofluorescence as described in methods. Images are Z-axis sections (0.4 μm) taken through a plane at the center of the tubule showing a cross-sectional view of cells in the lateral tubule walls (30, 31, 78). LPS increased p-ERK labeling, and this increase was eliminated by PD98059. Images are representative of at least eight tubules of each type. Scale bar = 5 μm. B: intensity of p-ERK staining for experiments in A was quantified as described in methods and is presented as a percentage of the control level. Bars are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 vs. control (ANOVA). C: time course of ERK activation. Inner stripe tissue from rats was incubated in vitro at 37°C in the absence and presence of LPS for the indicated times, and cell lysates were then immunoblotted with p-ERK antibody for analysis of ERK phosphorylation and anti-ERK antibody for total ERK level. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. D: p-ERK levels normalized for total ERK were determined for experiments in C by densitometry. p-ERK/ERK ratios are presented as a percentage of the control value (0 min) measured in the same experiment. Bars are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 min.