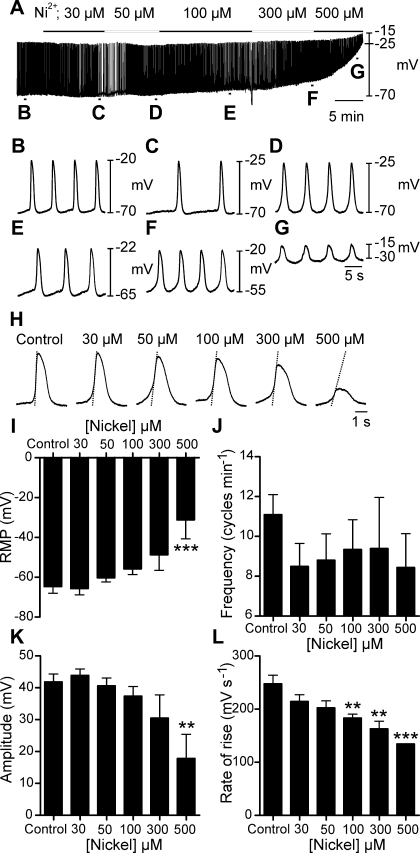
Fig. 5.
Effects of the T-type Ca2+ channel antagonist nickel on oviduct slow waves. A–G: dose-dependent effects of nickel (30–500 μM) on electrical activity. B–G: faster sweep speeds of sections indicated on the trace in A. H: individual slow waves at the maximal effect of each concentration of nickel. Superimposed lines on the upstroke phase of the slow waves indicate a dose-dependent decrease in the rate of rise. Nickel produced a depolarization in membrane potential and a reduction in the rate of rise of the slow wave upstroke. I–L: summaries of the dose-dependent effects of nickel on RMP (I), frequency (J), amplitude (K), and maximum rate of rise of the upstroke (L) plotted as a function of nickel concentration. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey test).