Fig. 1.
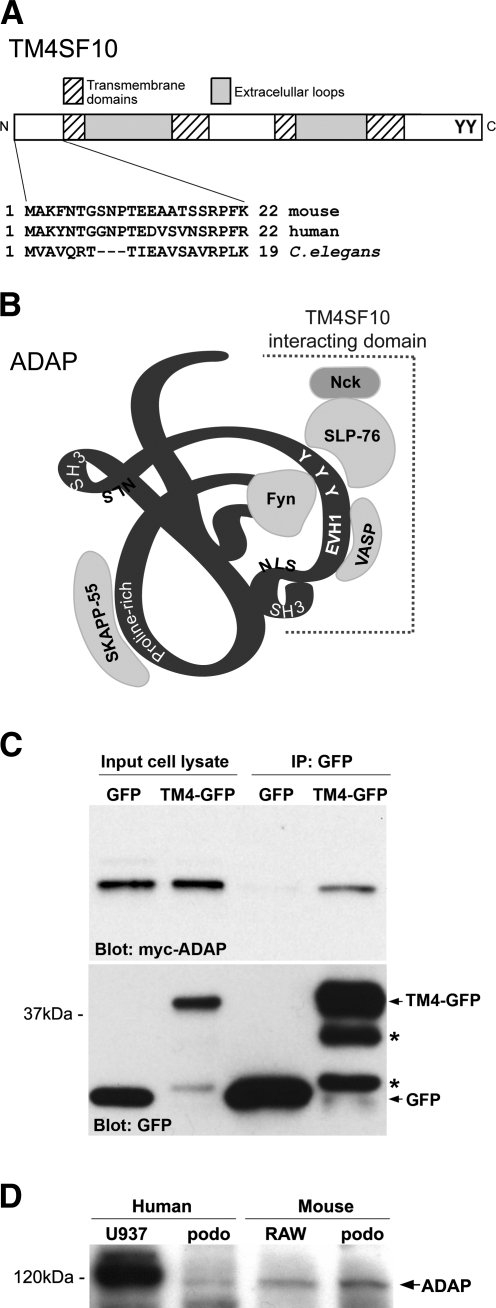
Adhesion and degranulation-promoting adaptor protein (ADAP) is a TM4SF10 [transmembrane tetra(4)-span family 10] interacting protein and is expressed in podocytes. A: schematic diagram of TM4SF10 protein domain structure noting the highly conserved 22 amino acid NH2-terminus (N) used as bait in the yeast two hybrid screen, the four trans-membrane domains typical of the tetraspanin proteins, and potential tyrosine phosphorylation sites on the COOH-terminus (C). B: schematic ribbon diagram of the 130-kDa ADAP protein (not drawn to scale) showing protein-protein interaction motifs (proline-rich, SH3, and EVH1), putative nuclear localization signal (NLS), and known tyrosine (Y) phosphorylation sites in addition to proteins that bind ADAP in lymphocytes (Fyn, VASP, SKAPP-55, and SLP-76 which also binds Nck). The region identified in the yeast two-hybrid screen and putative binding region for TM4SF10 is shown with the dashed line and span amino acids 378 to the COOH-terminus. C: Western blot of cell lysates from MDCK cells stably expressing GFP (lanes 1, 3) or TM4SF10-green fluorescent protein (GFP) (“TM4-GFP,” lanes 2, 4), and cotransfected with myc-ADAP. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies (lanes 3, 4) and blotted for myc (top) or GFP (bottom); *translationally truncated or proteolytically cleaved TM4SF10-GFP fusion proteins. D: Western blot of whole cell lysates from human and mouse podocyte (“podo”) cell lines confirming ADAP expression. Murine monocytic cell line RAW264.7 (RAW) and human monocytic cell line U937 were used as positive controls.