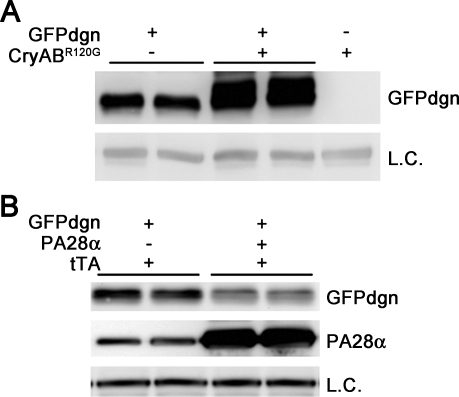
Fig. 3.
Use of GFPdgn reporter mice reveals proteasome functional insufficiency (PFI, A) and proteasome functional enhancement (B) in the heart. A: representative image of Western blot analyses for GFPdgn in the GFPdgn/CryABR120G double transgenic mouse heart, compared with littermate GFPdgn single transgenic mouse hearts. The soluble fraction of myocardial protein extracts from 1-mo-old mice of the indicated genotypes (top labels) were used for the analyses. PFI in the CryABR120G-based desmin-related cardiomyopathy mouse heart is revealed by the increased GFPdgn protein levels in the double transgenic mouse hearts. B: representative image of Western blot analyses for GFPdgn and proteasome activator 28α (PA28α) in the heart. Total proteins were extracted from ventricular myocardium of littermate mice of the indicated genotypes (labels at the top of the panel) at 8 wk of age and used for Western blot analyses for the indicated proteins. Note that GFPdgn protein levels were markedly decreased in PA28α overexpression hearts, indicating that proteasome proteolytic function in the heart is significantly enhanced by cardiomyocyte-restricted overexpression of PA28α. LC, loading control; tTA, tetracycline-controlled transactivator.