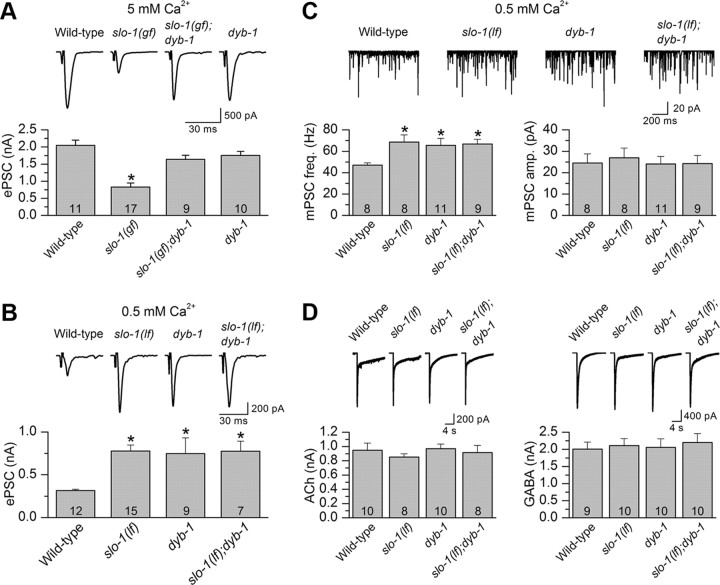
Figure 4.
DYB-1 was required by SLO-1 to control neurotransmitter release at NMJs. A, dyb-1 mutant counteracted the inhibitory effect of slo-1(gf) on ePSCs at 5 mm [Ca2+]o. B, The ePSC amplitude of dyb-1 mutant was significantly larger than that of the wild type but similar to that of slo-1(lf) or the slo-1(lf);dyb-1 double mutant. C, The frequency of mPSCs was increased, whereas the mean amplitude did not change in slo-1(lf), dyb-1, and slo-1(lf);dyb-1 compared with the wild type. D, Responses of body-wall muscle cells to exogenous ACh (100 μm) and GABA (100 μm) were unaltered in the mutants compared with the wild type. The holding potential for all recordings was −60 mV. *p < 0.05, significantly different from the wild type (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test). The number of samples analyzed is indicated inside each column.