Fig. 11.
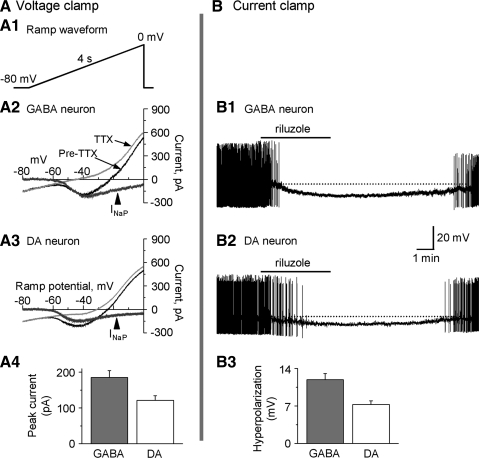
Persistent Na current (INaP) is larger in SNr GABA neurons than in SNc DA neurons. A: voltage clamp data on INaP. A1: diagram showing the voltage ramp waveform consisting of a 4-s ramp from −80 mV to 0 mV. A2 and A3: representative current traces before (black line) and after (thin gray line) perfusion of 1 μM tetrodotoxin (TTX) evoked by the voltage ramp, in GABA neurons (A2) and DA neurons (A3). TTX-sensitive INaP (thick gray line) was obtained by subtraction traces before after perfusion of 1 μM TTX. A4: pooled data of peak INaP in SNr GABA (n = 7) and SNc DA (n = 6) neurons. B: current clamp data on INaP. B1 and B2: representative traces showing the effects of 10 μM riluzole in SNr GABA neurons (B1) and SNc DA neurons (B2). Bath perfusion of 10 μM riluzole induced a stronger hyperpolarization in GABA neurons than in DA neurons. Spike amplitudes were truncated due to slow resampling (1 kHz) for reducing the large data size of long recording segments. B3: pooled data on 10 μM riluzole-induced hyperpolarization in SNr GABA neurons (n = 6) and SNc DA neurons (n = 5). The difference was significant (P < 0.05).