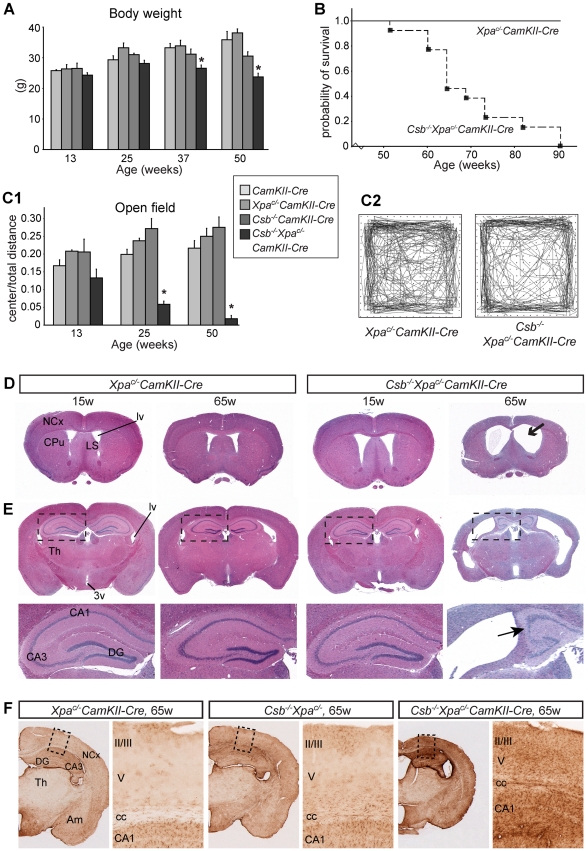
Figure 5. Reduced lifespan, age-dependent behavioral abnormalities, and brain atrophy in forebrain neuron-specific knockout of Xpa in Csb−/− mice.
A) Mean body weight of CamKIIα-Cre, Csb−/−CamKIIα-Cre, Xpa c/− CamKIIα-Cre and Csb−/−/Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre mice. Values are means ± SE (n = 8 to 13/group). Note the loss of body weight in Csbm/m/Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre mice after the age of 25 weeks. * represent P<0.05, as compared to other groups of the same age (one-way Anova with Tukey's post-test). B) Survival curve of Csb−/−/Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre mice (n = 13) as compared to wild type and single mutant littermates (combined n = 13). C) Representative examples of open field plots (C2) and quantification of the distance moved in the center as compared to total distance moved (C1), showing reduced ambulatory behavior of Csb−/−/Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre mice (n = 6) in the center of the field. Note that the center/total distance ratio is already reduced in 3 month-old Csbm/m/Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre mice, and decreases upon further aging. * in panel C, P<0.05, compared to other groups of the same age (one-way Anova with Tukey's post test). D, E) Coronal 4 µm thick, haematoxylin/eosin-stained paraffin sections of 15 and 65 week old Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre and Csb−/−/Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre mouse brains; sections grossly correspond to sections 0.5 to 1 mm anterior to the bregma (D) and 1.5 to 2 mm posterior to the bregma (E) as depicted in the mouse brain atlas of Paxinos and Franklin [85]. 65 week old Csb−/−/Xpa c/−/CamKIIα-Cre show dilated ventricles, and atrophy of the neocortex (NCx), hippocampus, the caudatus-putamen (CPu) and the septum. CA3, CA3 hippocampal subfields; DG, dentate gyrus; Th, thalamus; LS, lateral septum; lv, lateral ventricle. F) GFAP-immunoperoxidase staining in coronal brain sections of 65 week-old Xpa c/− CamKIIα-Cre, Csb−/− and Csb−/−Xpa c/− CamKIIα-Cre shows increased GFAP staining in the neocortex (NCx), hippocampus and amygdala of Csb−/−Xpa c/− CamKIIα-Cre mice. GFAP staining in the thalamus (Th) was the same as in Xpa c/− CamKIIα-Cre and Csb−/− mice.