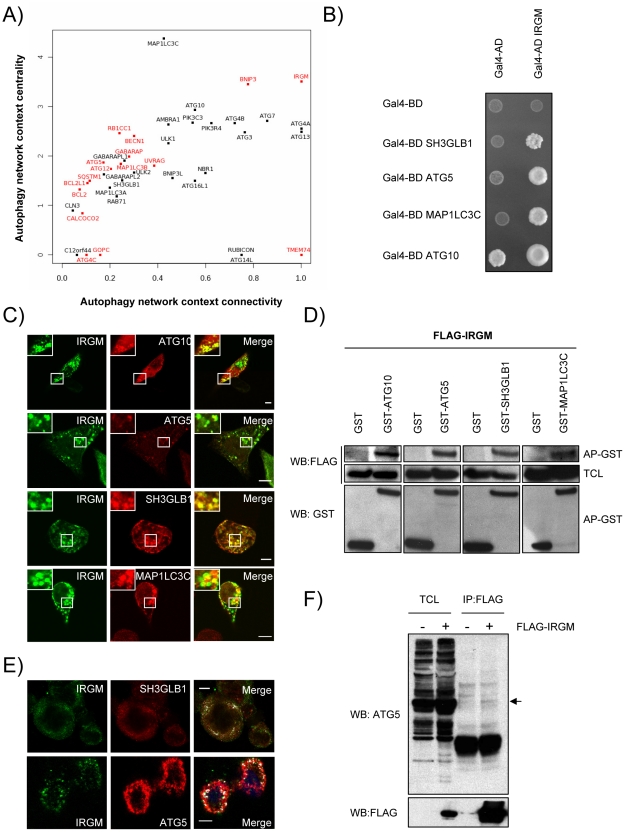
Figure 2. IRGM, a protein that is highly targeted by RNA viruses, co-localizes and interacts with several autophagy-associated proteins.
(A) Autophagy-associated proteins contribute differently to the autophagy network. Autophagy-associated proteins are plotted according to their context connectivity and context centrality. Autophagy context connectivity (x axis) is the ratio of interaction in autophagy network over the interaction in the whole human protein interaction network. Autophagy context centrality (y axis) is the ratio of betweenness (log normalized values) in autophagy network over the betweenness in the human protein interaction network. A protein with high degree and high betweenness ratios is respectively defined as highly devoted and highly central in the autophagy context. Proteins in red represent autophagy-associated proteins targeted by at least one RNA virus protein. The four proteins that are not connected to the autophagy network are not represented. (B) IRGM interacts with ATG10, ATG5, SH3GLB1 and MAP1LC3C. IRGM was tested by yeast two-hybrid against 35 different autophagy-associated proteins. Positive interactions with ATG10, ATG5, SH3GLB1 and MAP1LC3C were found. A reduced yeast two-hybrid matrix containing positive interactions and the appropriate empty vector controls is shown. One experiment representative of three is shown. (C) IRGM co-localizes with autophagy-associated proteins. GFP-IRGM was expressed in HeLa cells together with FLAG-ATG10, FLAG-ATG5, FLAG-SH3GLB1 or FLAG-MAP1LC3C. Fixed cells were then stained with an anti-FLAG antibody and GFP-IRGM and FLAG-tagged proteins co-localisation was visualized on merged images by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 5 µM. (D) IRGM interacts with autophagy-associated proteins. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with GST and GST-tagged expression vectors encoding the indicated proteins and FLAG-IRGM. Interaction was assayed by co-affinity purification (AP) using glutathione-sepharose beads. FLAG-IRGM was detected using anti-FLAG antibody after (AP-GST, WB: FLAG) and before (total cell lysate-TCL, WB: FLAG) co-AP. GST alone and GST-tagged proteins were detected by using anti-GST antibody (AP-GST, WB: GST). One experiment representative of two is shown. (E) Endogenous IRGM co-localizes with endogenous SH3GLB1 and ATG5 in MeV infected cells. HeLa cells were infected with MeV Edmonston (MOI = 1) for 24 hrs. Cells were fixed in acetone and both IRGM and/or SH3GLB1 or ATG5 were detected using specific antibodies. IRGM/SH3GLB1 or IRGM/ATG5 protein co-localisation was visualized on merged images obtained by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 5 µM. (F) Endogenous ATG5 interacts with FLAG-IRGM. HeLa cells were transfected or not with FLAG-IRGM encoding vector and infected with MeV (MOI = 1) 24 hrs post-transfection. Cells were lysed 24 hrs post-infection. Flag-tagged IRGM was immunoprecipitated and endogenous ATG5 binding was detected by western blot (top panel). Overexpression and immunoprecipitation of FLAG tagged IRGM was confirmed by a western blot using (bottom panel).