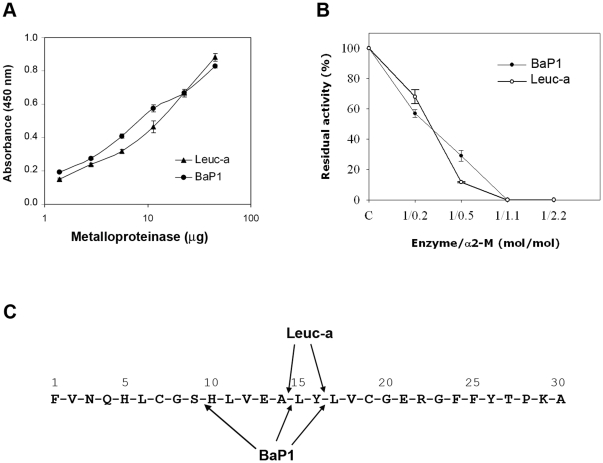
Figure 2. Proteolytic activity of BaP1 and leuc-a, and inhibition by α2-macroglobulin.
(A) Hydrolytic activity of BaP1 and leuc-a on azocasein. Various amounts of each enzyme were incubated with azocasein for 90 min at 37°C. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 5% trichloroacetic acid, and the absorbances of the supernatants at 450 nm were recorded after centrifugation. Controls of azocasein without enzyme were run in parallel and their absorbance was subtracted from the sample values. Results are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). (B) Stoichiometry of inhibition of BaP1 and leuc-a by α2M. The plasma inhibitor was incubated with BaP1 or leuc-a at various molar ratios, and proteolytic activity was tested on dimethylcasein. The remaining protease activity is expressed as percentage of the original activity measured in the absence of the inhibitor. Results are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (C) Cleavage sites of BaP1 and leuc-a on oxidized insulin B-chain. After 30 min of digestion, peptides were separated by HPLC and identified by their amino acid sequence.