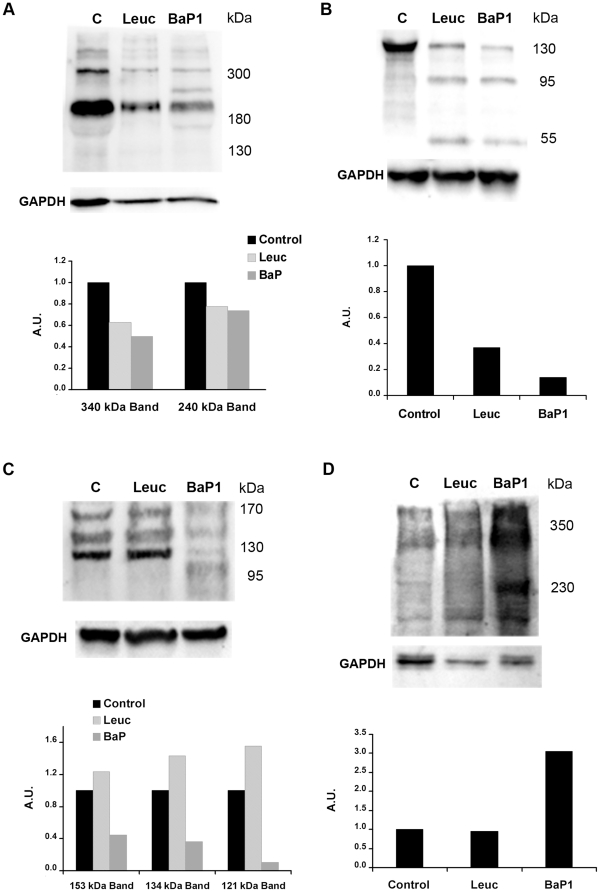
Figure 5. Hydrolysis of basement membrane components in vivo.
Hydrolysis of laminin (A), nidogen (B), type IV collagen (C) and perlecan (D) by BaP1 and leuc-a, as detected by Western blotting of homogenates of injected mouse gastrocnemius muscle. Groups of mice were injected in the gastrocnemius muscle with either 50 µg BaP1, 50 µg leuc-a or PBS (lane C). After 15 min, mice were sacrificed and tissue was homogenized and centrifuged to obtain the supernatant. Supernatants of muscle homogenates were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, using a 4–15% gradient gel, and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Immunodetection was performed with either anti-laminin, anti-nidogen, anti-type IV collagen or anti-endorepellin antibodies, and with anti-GAPDH as loading control in tissue homogenates. Reaction was developed with a chemiluminiscent substrate. Densitometry was carried out in blots of tissue homogenates with ImageLab software; a relative quantification was performed adjusting each sample to the corresponding control.