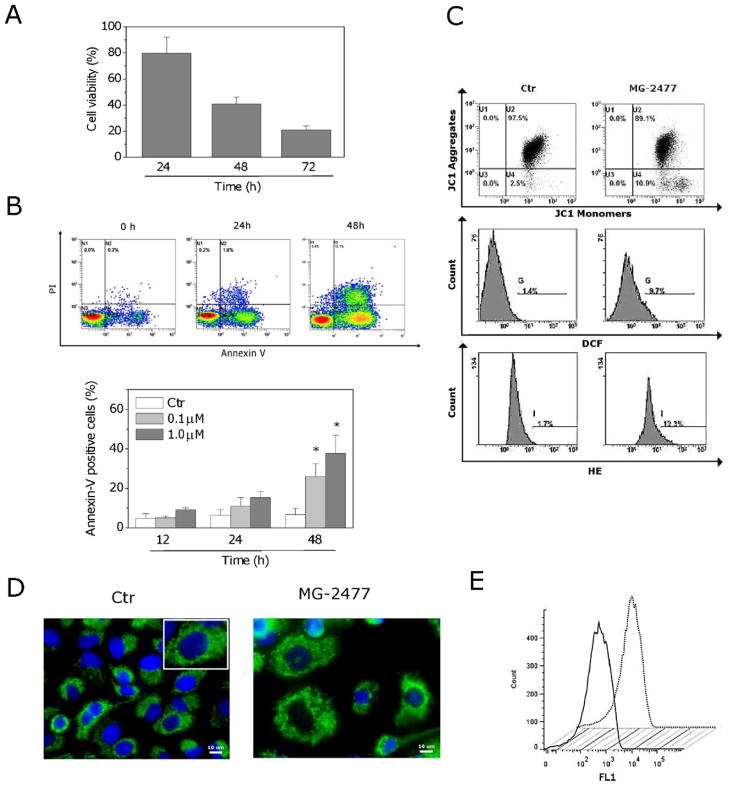
Fig. 4.
MG-2477 induced delayed apoptosis in A549 cells. (A) Cells were incubated with 1 μM MG-2477 for the indicated times. Cell viability was quantified by the MTT assay. (B) Representative histograms of A549 cells treated with MG-2477 (upper panel) and analyzed by flow cytometry after double staining of the cells with Annexin-V-FITC and PI (lower panel). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of six independent experiments. *p < 0.01 vs. control. (C) Analysis of mitochondrial dysfunction in cells treated with 1 μM MG-2477 for 48 h and analyzed by flow cytometry for mitochondrial depolarization. Cells were labeled with the dye JC-1, which measures depolarization. ROS production was measured after labeling the cells with the fluorescent probes H2DCFDA and HE. (D) Representative confocal images of control A549 cells and cells treated with 1 μM MG-2477 for 48 h, showing cytochrome c labeled with a monoclonal antibody conjugated to FITC. The nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. Inset in the control cells image: an enlargement of one cell for a better comparison with the treated cells. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of cytochrome c after treatment with MG-2477 (1 μM) for 48 h. Cells were stained with a FTIC-conjugated monoclonal antibody directed against cytochrome c. Straight line: control cells; dotted line: MG-2477 treated cells. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of the article.)