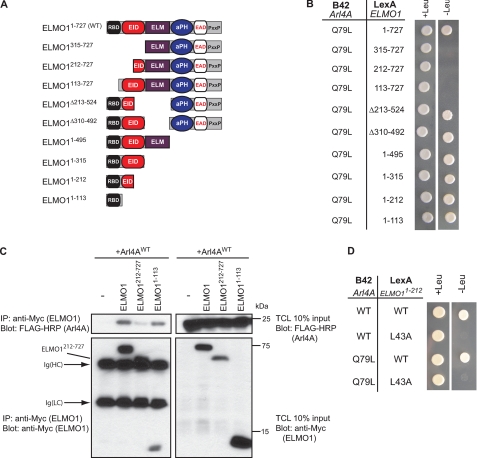
FIGURE 2.
Arl4A binds the ELMO1 RBD through a key evolutionarily conserved RBD residue. A, schematic representation of ELMO1 deletion mutants used in yeast two-hybrid experiments. B, the ELMO1 N terminus is required for Arl4A binding. Yeast strain EGY48 cotransformed with LexA BD fusion construct of ELMO1WT and deletion mutants, and the B42 fusion constructs of the indicated Arl4As were grown on selective (−histidine, −tryptophan, −leucine) and nonselective (−histidine, −tryptophan) medium for a nutrient selective growth assay. C, the Arl4A-ELMO1 interaction in cellulo requires the ELMO1 RBD. HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were cross-linked, lysed, and immunoprecipitated (IP) with an antibody against the Myc epitope (ELMO1). The coprecipitation of the various ELMO1 proteins and Arl4A was analyzed via immunoblotting with anti-Myc (ELMO1) and anti-FLAG-HRP (Arl4A) antibodies, respectively. D, mutation of a key conserved residue in the ELMO RBD (L43A) abolishes Arl4A binding. Yeast strain EGY48 cotransformed with LexA BD fusion construct of ELMO1WT and ELMO1L43A and the B42 fusion construct of Arl4AWT were grown on selective (−histidine, −tryptophan, −leucine) and nonselective (−histidine, −tryptophan) medium for a nutrient selective growth assay.