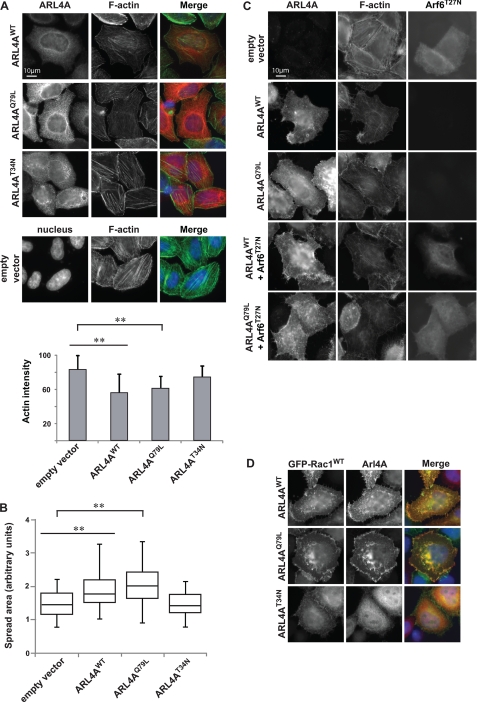
FIGURE 4.
Arl4A induces cytoskeletal changes in an Arf6-independent manner. A, overexpression of Arl4AWT and Arl4AQ79L alters actin structure in HeLa cells, but Alr4AT34N does not. Wild-type and active Arl4A were overexpressed in HeLa cells and stained for Arl4A (red) and phalloidin (green) using anti-Arl4A and Fluor 488 phalloidin, respectively. The bar chart indicates quantification results for each condition. The area of each cell was delineated, and the average fluorescence intensity of Fluor 488 phalloidin was measured in pixels using ImageJ (National Institutes of Health). More than 40 cells were assessed in each experiment, and the data are the means ± S.E. of at least triplicate experiments. Student's t test was performed to compare each condition (**, p < 0.01). Scale bar, 10 μm. B, expression of Arl4AWT and ARL4AQ79L promotes cell spreading on fibronectin. For quantification, the area of each cell was delineated, and more than 40 cells were estimated for each condition using ImageJ. The box plot shows the distribution of cell size for each condition. Student's t test was performed to compare each condition (**, p < 0.01). C, coexpression of dominant negative Arf6 (Arf6T27N) with Arl4AWT or Arl4AQ79L does not fully hinder actin cytoskeletal reorganization. HeLa cells were cotransfected with Arf6T27N and either Arl4AWT or Arl4AQ79L. Transfected cells were fixed and stained with anti-Arl4A and anti-Arf6 antibodies. Scale bar, 10 μm. D, ARL4AWT and Arl4AQ79L colocalize with GFP-Rac1WT at membrane ruffles. Arl4AT34N fails to relocalize GFP-Rac1WT and to promote membrane ruffles. Transfected cells were fixed and stained with anti-Arl4A.