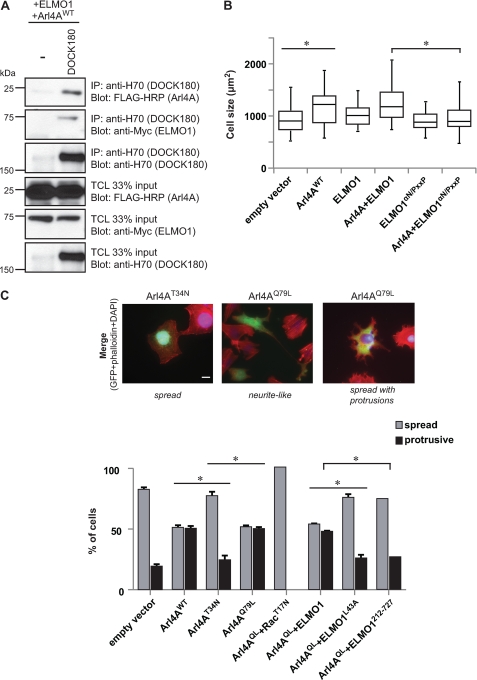
FIGURE 5.
Arl4A induces cellular protrusions through an ELMO-DOCK180-Rac signaling module. A, ELMO is the common denominator for DOCK180-ELMO1-Arl4A trimeric complex formation. HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were subject to a cross-linker, lysed, and immunoprecipitated (IP) with H-70 (DOCK180). The coprecipitation of DOCK180, ELMO1 WT and mutants, and Arl4A was analyzed via immunoblotting with anti-H-70 (DOCK180), anti-Myc (ELMO1), and anti-FLAG-HRP (Arl4A) antibodies, respectively. B, Arl4A signaling induces cell spreading through an ELMO-DOCK180 pathway. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were fixed and stained with anti-Arl4A and anti-Myc antibodies (ELMO1). The box plot shows the distribution of cell size for each condition. The size of more than 20 transfected cells for each condition was measured by ImageJ (*, p < 0.05). C, quantification of the effect on cell morphology in response to overexpression of Arl4A and other proteins. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids, and cell morphology was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Several independent fields were photographed at a magnification of 40×, and cells were scored for two phenotypes: spread (clearly spread and flat cells) and spread with protrusions (subdivided into (i) protrusive and (ii) neurite-like elongated cells). For each condition, >35 cells were measured. Analysis of variance tests and Bonferroni's multiple comparison was performed to compare each condition (*, p < 0.05; error bars represent S.E., n = 3). Scale bar, 20 μm.