FIGURE 5.
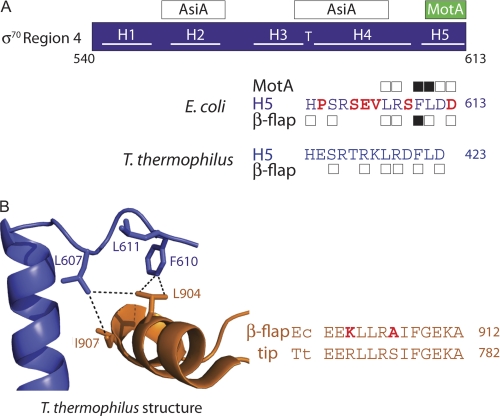
σ70 H5 residues important for interaction with the β-flap tip and MotANTD. A, schematic of σ70 Region 4, showing locations of interactions with AsiA and MotA. The C-terminal sequence (residues 600–613) of E. coli σ70 is shown. Boxes above/below the sequence denote residues where alanine substitutions decrease the interaction of Region 4 with MotANTD or the β-flap by 2-fold or more in the two-hybrid assays (Fig. 2); black boxes denote residues that also affect MotA/AsiA activation (Fig. 3) or promoter clearance (Fig. 4). The corresponding H5 sequence of T. thermophilus is shown below; σ residues that are within 5 Å of the β-flap in the T. thermophilus structure (2) are denoted with a box. B, left, portion of the structure of the T. thermophilus RNAP depicting interactions between the C terminus of σ in blue and the β-flap tip in orange (Protein Data Bank code 1IW7) (2). Stick renderings of residues discussed in the text, which are identical between E. coli and T. thermophilus RNAP, are shown and numbered according to E. coli RNAP (E. coli/T. thermophilus numbering: σLeu-607/Leu-418, σPhe-610/Phe-421, σLeu-611/Leu-422, βLeu-904/Leu-774, βIle-907/Ile-777). Dashed lines indicate distances <5 Å. B, right, alignment of H5 sequences and β-flap tip sequences in E. coli (Ec) and T. thermophilus (Tt). E. coli residues that differ from those in T. thermophilus are colored in red.