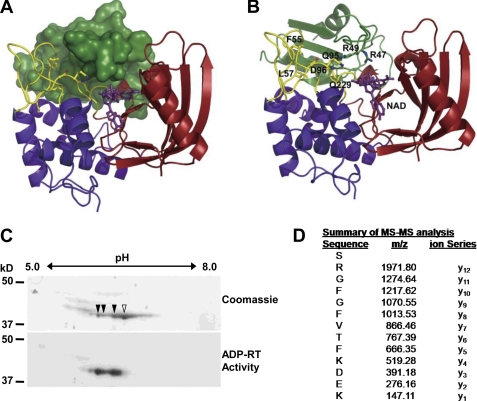
FIGURE 3.
Arginine 49 of GRP7 is ADP-ribosylated by HopU1. A, structure model of HopU1-NAD-GRP7-RRM complex. HopU1 is shown in ribbon representation, and the N-terminal domain is colored in blue, C-terminal domain in red, and protruding loops L1 and L4 are shown in yellow. GRP7-RRM (dark green) is shown in surface representation, and NAD (purple) is shown in stick representation. B, structure model with GRP7-RRM shown as ribbon representation. Critical HopU1 residues for interaction with GRP7 and potential ADP-ribosylation sites Arg-47 and Arg-49 are indicated in stick representation. C, two-dimensional PAGE gels of in vitro mADP-RT reactions containing purified HopU1-His, GRP7-GST, and 32P-labeled NAD stained with Coomassie Blue to visualize total protein or exposed to autoradiography film to identify 32P-labeled proteins. Protein spots labeled with 32P corresponding to ADP-ribosylated proteins are marked with filled arrowheads, and the unlabeled spot is marked with an open arrowhead. D, mass spectrometric analyses of tryptic peptides derived from the above mADP-RT reactions using nonradioactive NAD. All spots corresponding to the indicated spots in B were cut out and sent for MS/MS. One fragment shown contained a higher molecular mass than predicted. The molecular mass of the arginine (y12) corresponds to Arg-49 of GRP7 and was equal to ADP-ribosylated arginine, indicating that this residue was ADP-ribosylated by HopU1.